Viptela Control Plane Setup
published: 22nd of March 2018
Intro
Viptela is an SDWAN platform now owned by Cisco. In this blog I will setup a Viptela control plane using self signed certificates for the purpose of testing in a lab environment.
The recommended mode of operation for production deployments is using Symantec signed certificates that are managed by Viptela. Using Viptela issued certificates allows for ZTP and greatly simplifies the lifecycle management of certificates as it is all handled by Viptela and their software.
The one caveat to using Viptela issued certificates is that you need to raise a case to have the controller certificates signed. This is fine for a production deployment where you do it once and forget about it, but it does not really work in a lab where you spin up/down environments for the purpose of testing infrastructure as code and testing code against infrastructure.
Lab Topology

Lab IP Addressing
| Host | VPN 0 | VPN 512 |
|---|---|---|
| vManage | 10.10.100.31/24 | 172.16.100.31/24 |
| vBond | 10.10.100.32/24 | 172.16.100.32/24 |
| vSmart | 10.10.100.33/24 | 172.16.100.33/24 |
| vEdge | 10.10.100.34/24 | 172.16.100.34/24 |
Lab Software
- vManage - 16.3.2 / 17.2.0
- vBond - 16.3.2 / 17.2.0
- vSmart - 16.3.2 / 17.2.0
- vEdge - 17.2.0
This lab assumes that you already have the virtual machine images booted in your hypervisor platform of choice. I am personally running this lab in OpenStack, but you can just as easily boot the VM's in VMware ESX/Fusion/Workstation or with a bit if fiddling Virtualbox or KVM.
The controllers will start on software version 16.3.2 and be upgraded to 17.2.0 during the course of the lab.
Controllers
The Viptela control plane consists of the following components.
vManage NMS
The vManage is the central point of configuration and monitoring for the Viptela solution.
vBond Orchestrator
The vBond authenticates and validates devices that join the overlay network.
vSmart Controller
The vSmart controller is the point of control over the routing policy in the overlay network. vSmart controllers are similar to BGP route reflectors.
CLI Modes
Viptela devices use an ubuntu 1404 base operating system. There are two cli modes to be aware of when working with Viptela device software; the vshell and the viptela-cli . When you login to a Viptela device terminal you are placed in the viptela-cli .
viptela-cli
The viptela-cli is similar to a Cisco IOS terminal with nicer features like candidate config and commit style management.
# viptela-cli
vmanage#vshell
To logon to the vshell use the vshell command (Shocking right!). The vshell is very similar to a bash shell.
vmanage# vshell
# vshell
vmanage:~$To exit out of the vshell and return to the viptela-cli use the exit keyword.
vmanage:~$ exit
exit
vmanage#This lab will use both the viptela-cli and the vshell . If you are following along, please take note of which shell the commands are executed in.
Configuration
Lets get cracking with the configuration. In this lab we will start by configuring the root CA, then move onto installing certificates on the Viptela devices and finally upgrade the vManage, vSmart and vBond to code version 17.2.0 to allow the virtual vEdge to join the control plane.
vManage
Login to the vManage web interface with the username and password admin and navigate to the settings page.
Enter the organization name network-lab .
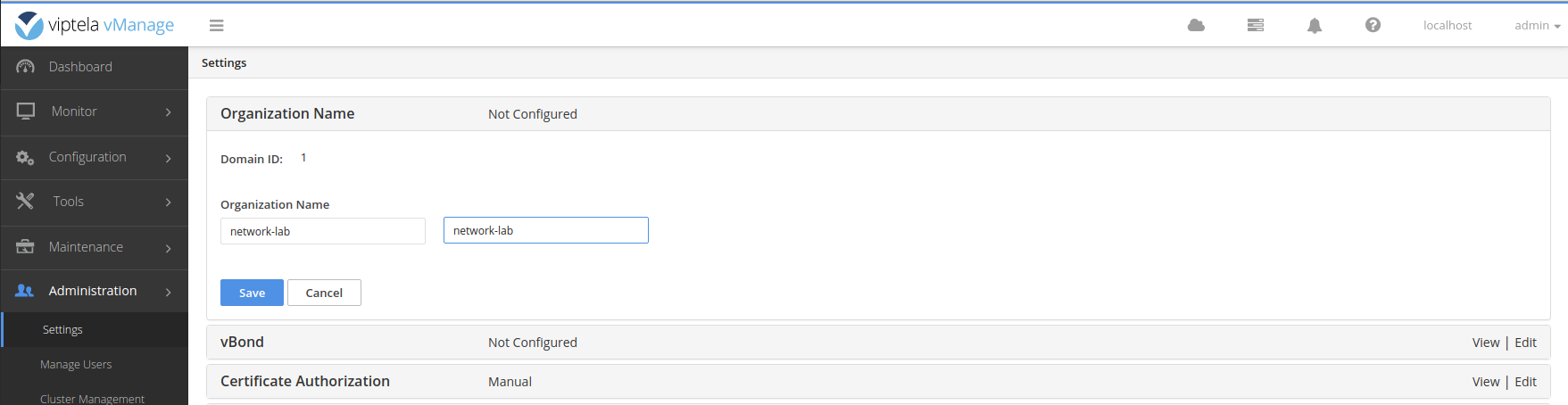
Also enter the vBond IP address 10.10.100.32 .
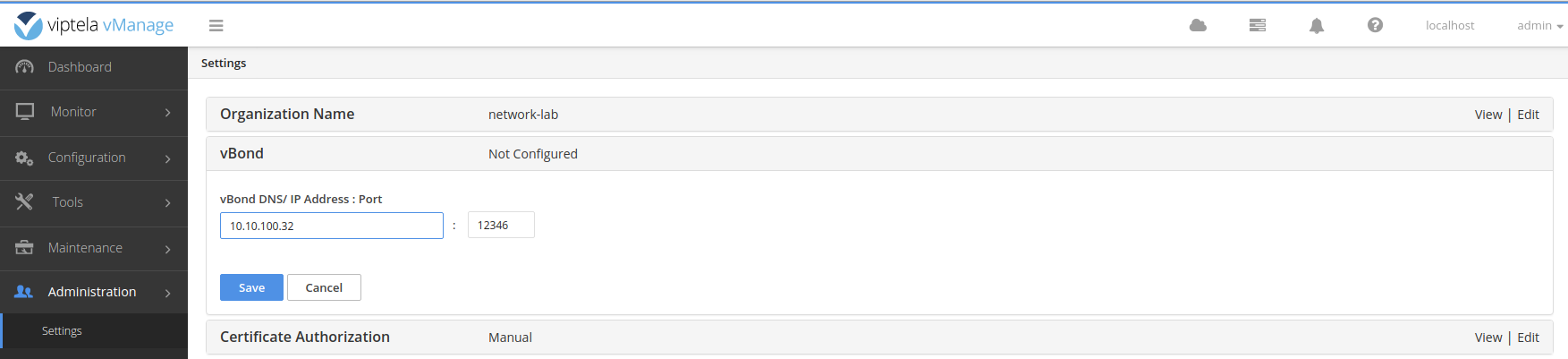
Bootstrap Config
Apply the following bootstrap configs to the hosts.
vManage
# viptela-cli
system
system-ip 1.1.1.1
site-id 1000
organization-name "network-lab"
vbond 10.10.100.32
!
vpn 0
interface eth1
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!
!
vpn 512
interface eth0
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!vBond
# viptela-cli
system
system-ip 1.1.1.2
site-id 1000
organization-name "network-lab"
vbond 10.10.100.32 local vbond-only
!
vpn 0
interface ge0/0
ip dhcp-client
ipv6 dhcp-client
no shutdown
!
!
vpn 512
interface eth0
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!vSmart
# viptela-cli
system
system-ip 1.1.1.3
site-id 1000
organization-name "network-lab"
vbond 10.10.100.32
!
vpn 0
interface eth1
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!
!
vpn 512
interface eth0
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!vEdge
# viptela-cli
system
system-ip 3.1.1.1
site-id 1
organization-name "network-lab"
vbond 10.10.100.32
!
vpn 0
interface ge0/0
ip dhcp-client
ipv6 dhcp-client
tunnel-interface
encapsulation ipsec
no allow-service bgp
allow-service dhcp
allow-service dns
allow-service icmp
no allow-service sshd
no allow-service netconf
no allow-service ntp
no allow-service ospf
no allow-service stun
!
no shutdown
!
!
vpn 512
interface eth0
ip dhcp-client
no shutdown
!Certificate Server
For this lab I will use the vManage as the root certificate authority. I will utilize the openssl command to generate and sign certificates from the vshell terminal.
Generate a root CA key named ROOTCA.key .
# vshell
openssl genrsa -out ROOTCA.key 2048
# output
Generating RSA private key, 2048 bit long modulus
.....................................................+++
................+++
e is 65537 (0x10001)Generate a ROOTCA.pem certificate and sign it with the ROOTCA.key key.
# vshell
openssl req -x509 -new -nodes -key ROOTCA.key -sha256 -days 1024 \
-subj "/C=AU/ST=NSW/L=NSW/O=network-lab/CN=vmanage.lab" \
-out ROOTCA.pemExit out of the vshell and install the ROOTCA.pem certificate from the viptela-cli .
# viptela-cli
request root-cert-chain install /home/admin/ROOTCA.pem
# output
Uploading root-ca-cert-chain via VPN 0
Copying ... /home/admin/ROOTCA.pem via VPN 0
Successfully installed the root certificate chainIn the web interface generate a certificate signing request.
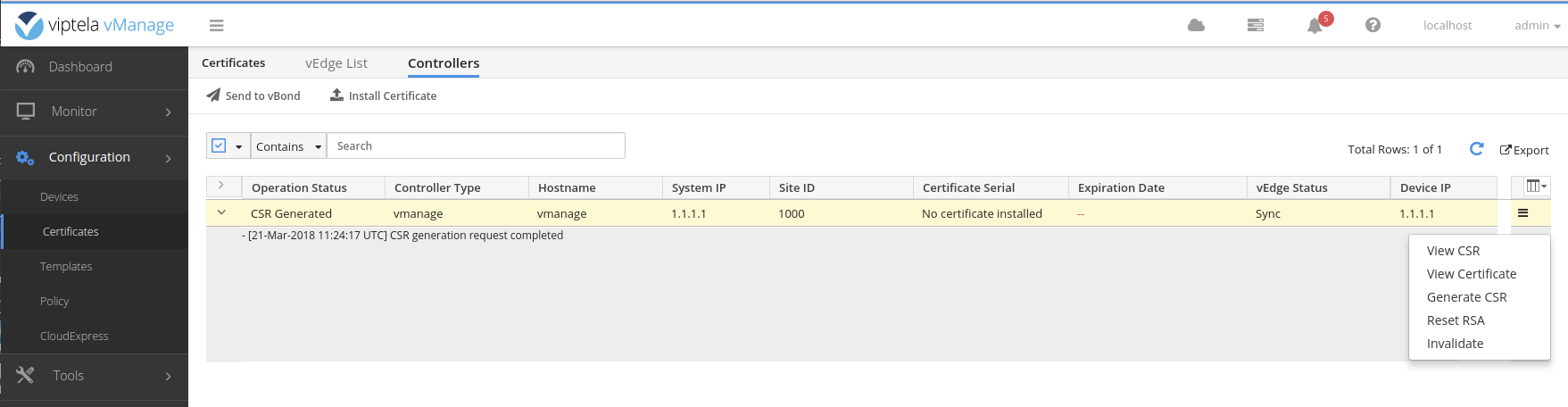
A window will popup with the CSR text. In the vshell use vim to create a file named vmanage.csr with the text from the popup.
Sign the vmanage.csr file with the ROOTCA.key
# vshell
openssl x509 -req -in vmanage.csr \
-CA ROOTCA.pem -CAkey ROOTCA.key -CAcreateserial \
-out vmanage.crt -days 500 -sha256
# output
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=San Jose/OU=network-lab/O=vIPtela Inc/CN=vmanage_613e7c7c-07f8-443b-aa90-969bf12a64e4_0.viptela.com/emailAddress=support@viptela.com
Getting CA Private KeyUse the cat command to view the contents of the vmanage.crt file and install the certificate in the web interface.
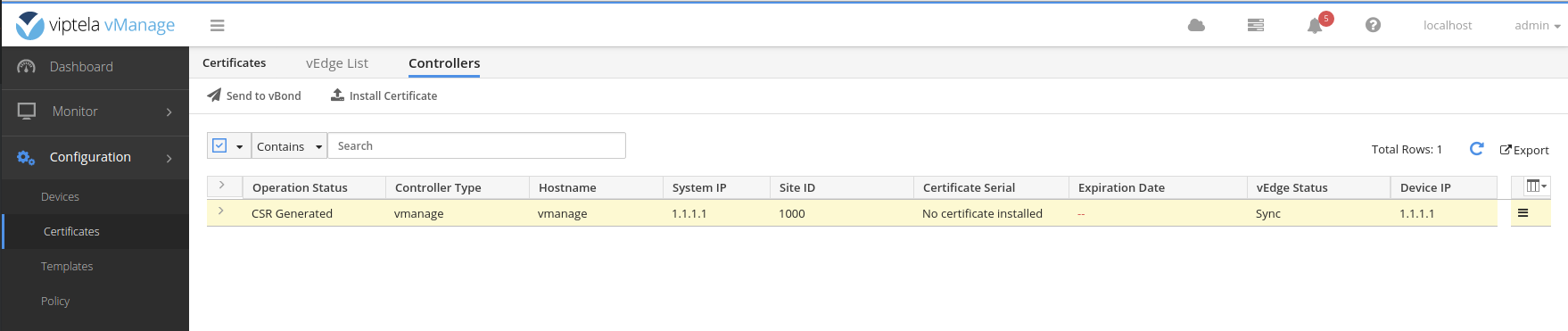
Paste the contents into the popup
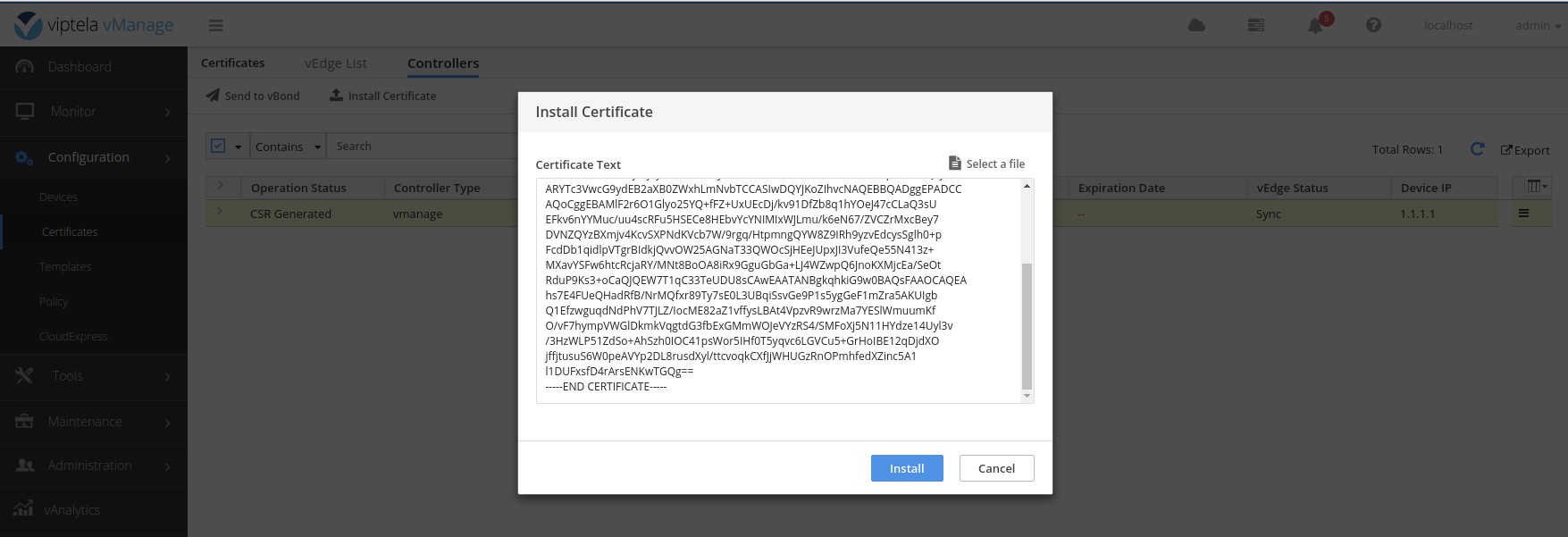
Sample successful certificate install log
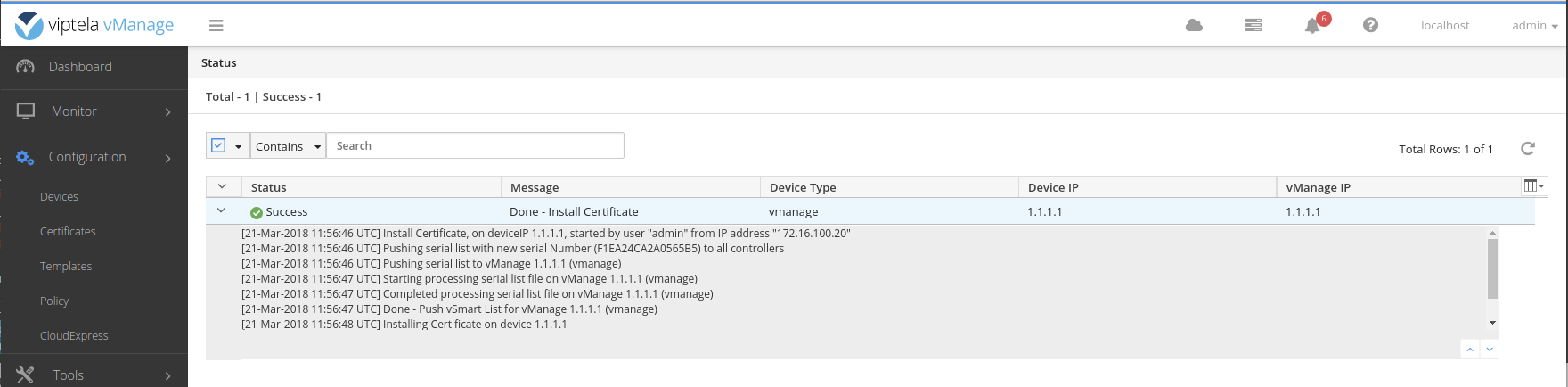
Finally, from the vshell install the vmanage.crt certificate
# viptela-cli
request certificate install /home/admin/vmanage.crt
# output
Installing certificate via VPN 0
Successfully installed the certificatevBond
Add the ROOTCA.pem certificate to the vBonds root certificate chain.
# viptela-cli
request root-cert-chain install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem vpn 512
# output
Uploading root-ca-cert-chain via VPN 512
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
ROOTCA.pem 100% 1269 2.4MB/s 00:00
Successfully installed the root certificate chainAdd the vBond to vManage web interface
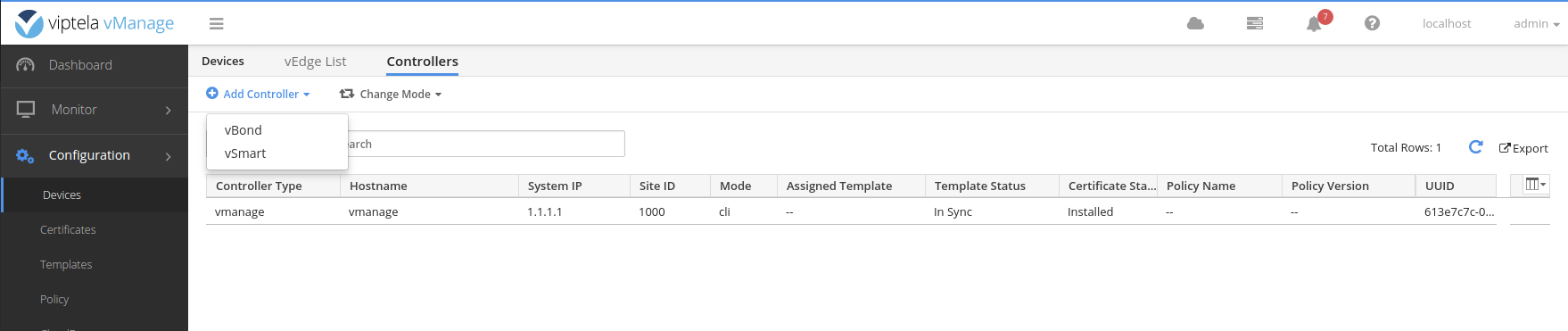
Enter the IP address of the vpn0 interface: 10.10.100.32 .
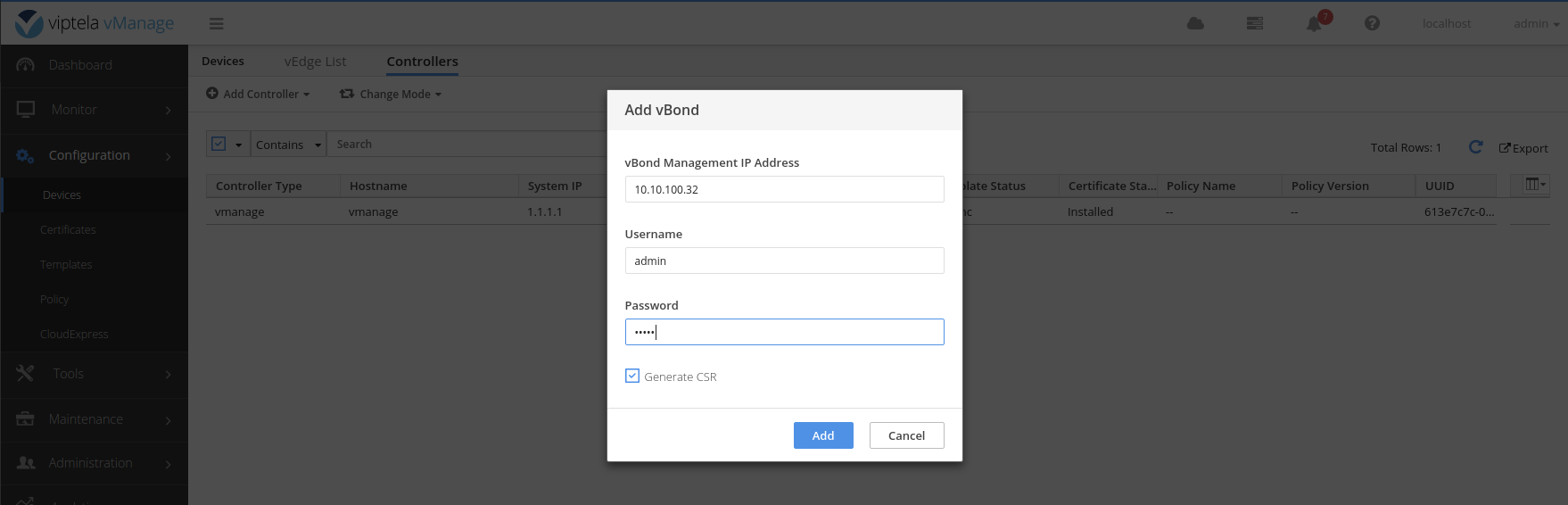
Example successfully added vBond.
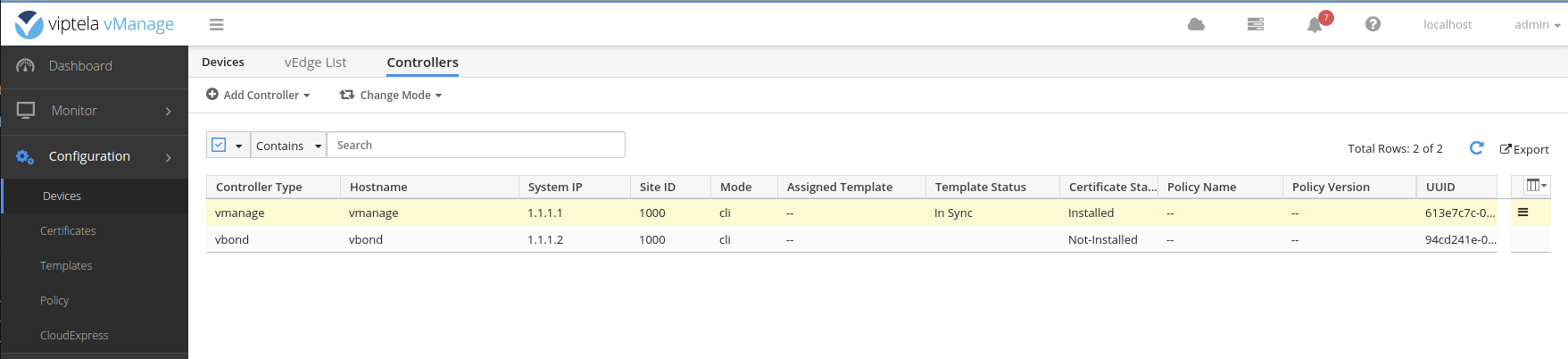
Get a copy of the vBond CSR text.
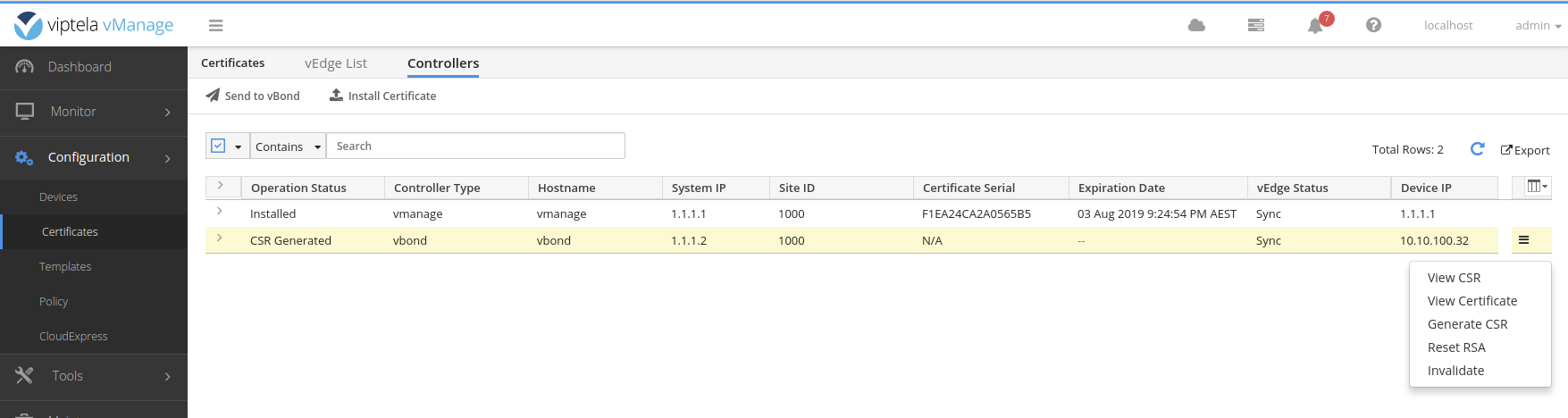
A window will popup with the CSR text. In the vshell on the vManage use vim to create a file named vbond.csr with the text from the popup.
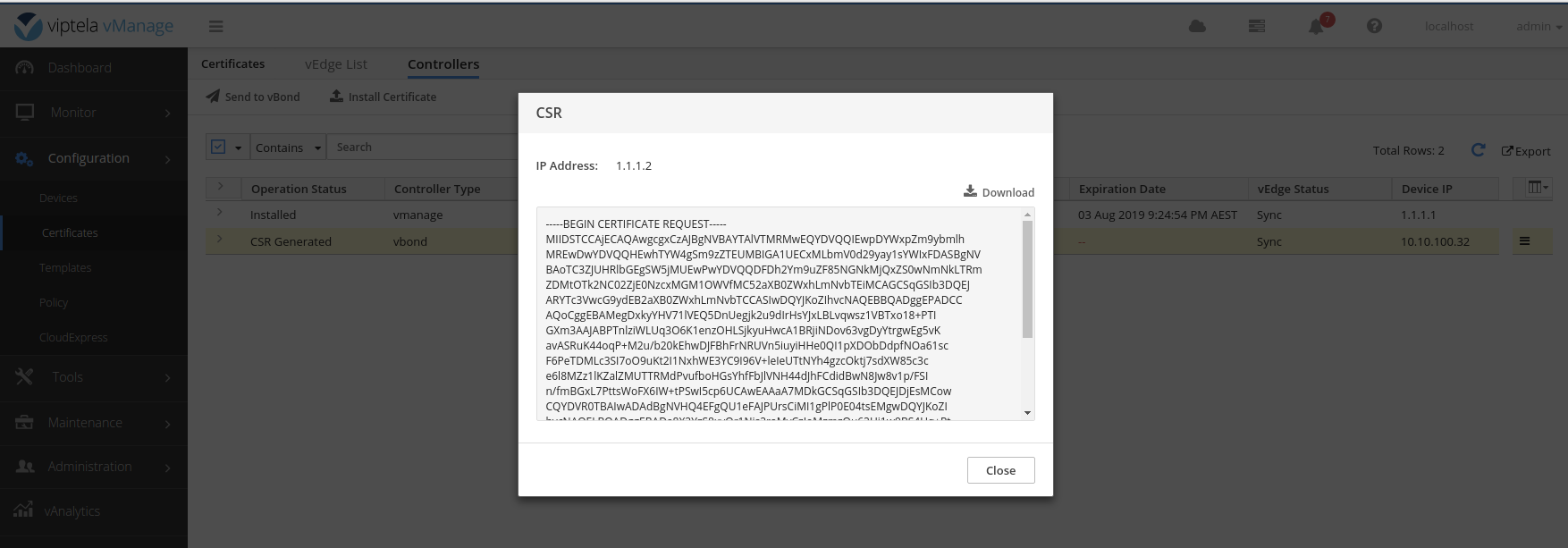
Sign the vbond.csr file with the ROOTCA.key
# vshell
openssl x509 -req -in vbond.csr \
-CA ROOTCA.pem -CAkey ROOTCA.key -CAcreateserial \
-out vbond.crt -days 500 -sha256
# output
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=San Jose/OU=network-lab/O=vIPtela Inc/CN=vbond_94cd241e-06cd-4fd3-9964-6f147710c59e_0.viptela.com/emailAddress=support@viptela.com
Getting CA Private KeyUse the cat command to view the contents of the vbond.crt file and install the certificate in the web interface.
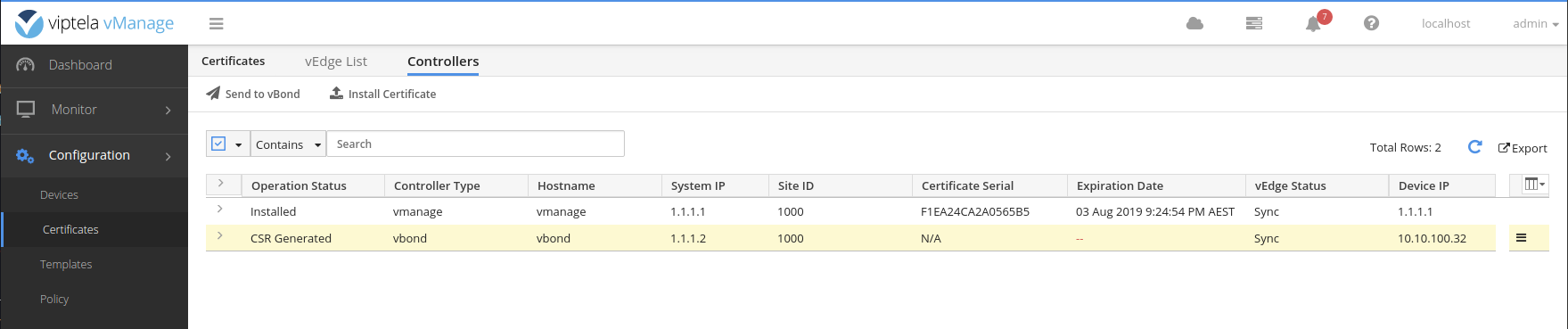
Paste the contents into the popup

Sample successful certificate install log
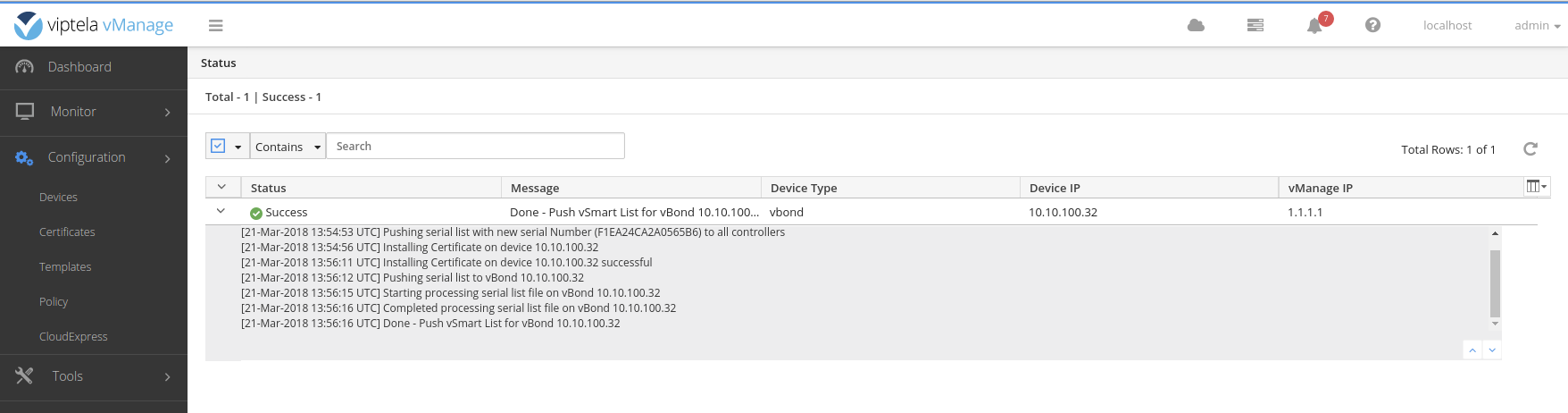
Send the list of certs to the vBond.
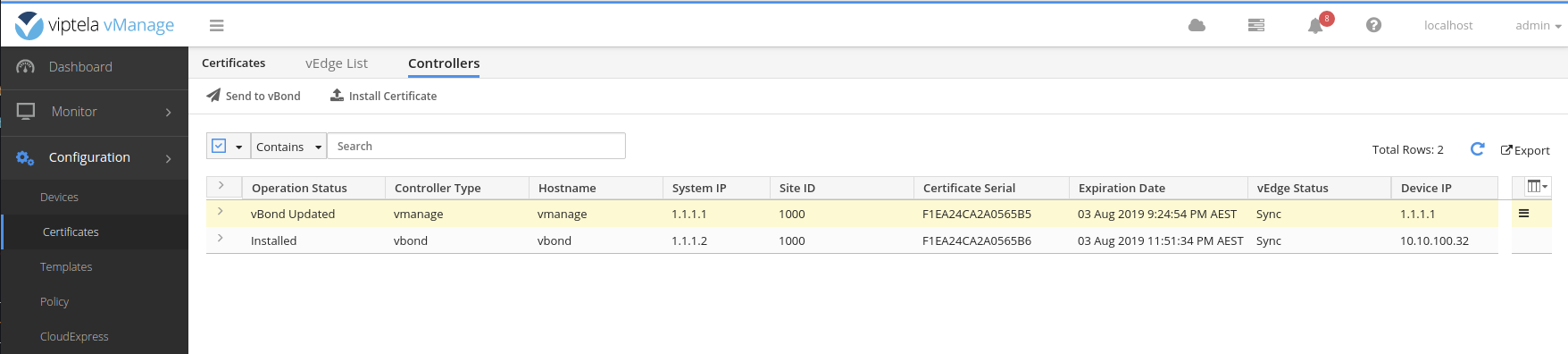
Example successfully updated vBond.
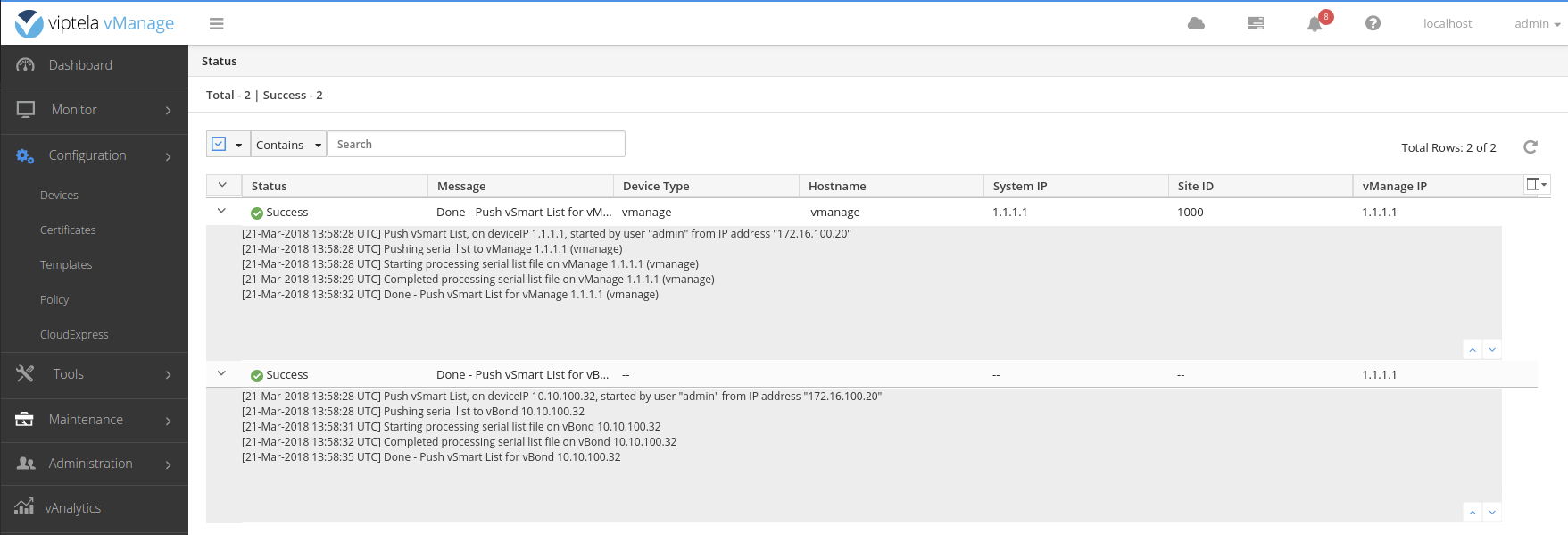
Finally, on the viptela-cli of the vBond install the vbond.crt certificate
# viptela-cli
request certificate install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vbond.crt vpn 512
# output
Installing certificate via VPN 512
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vbond.crt via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
vbond.crt 100% 1310 2.5MB/s 00:00
Successfully installed the certificatevSmart
Add the ROOTCA.pem certificate to the vSmarts root certificate chain.
# viptela-cli
request root-cert-chain install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem vpn 512
# output
Uploading root-ca-cert-chain via VPN 512
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
ROOTCA.pem 100% 1269 1.9MB/s 00:00
Successfully installed the root certificate chainAdd the vSmart to vManage web interface
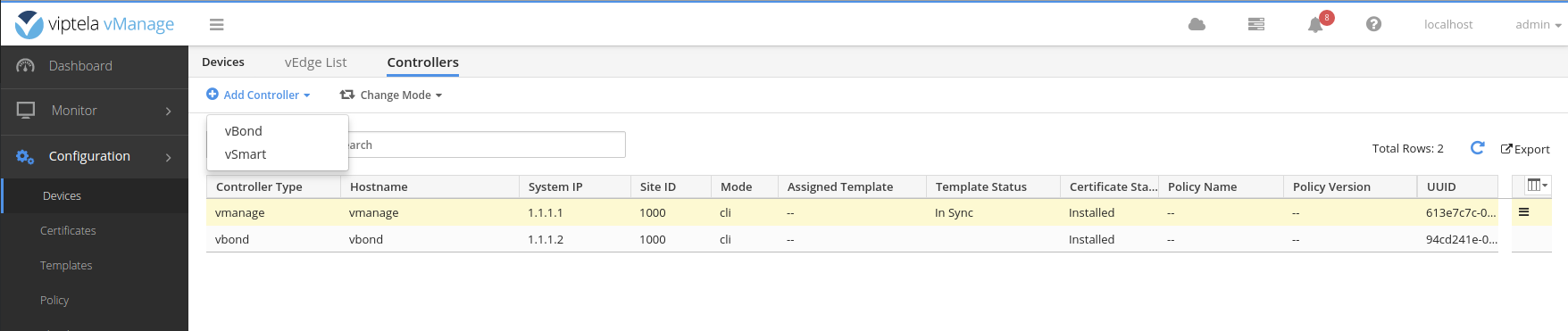
Enter the IP address of the vpn0 interface: 10.10.100.33 .
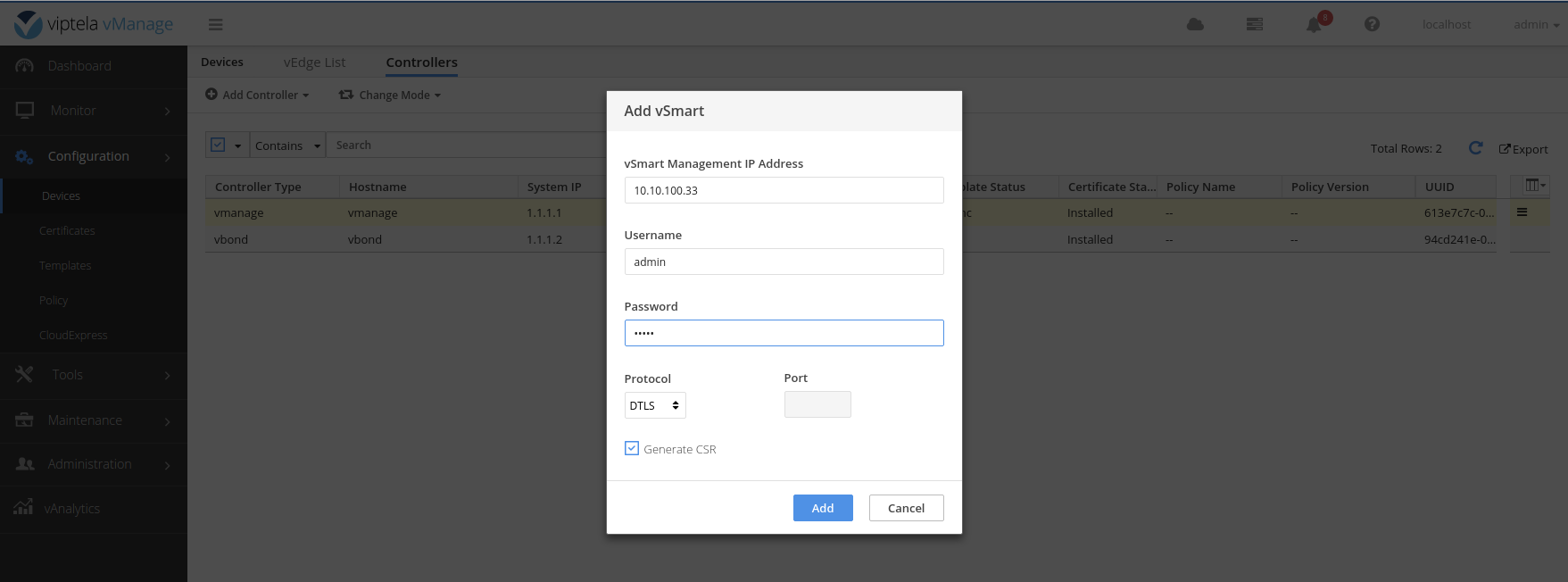
Get a copy of the vSmart CSR text.
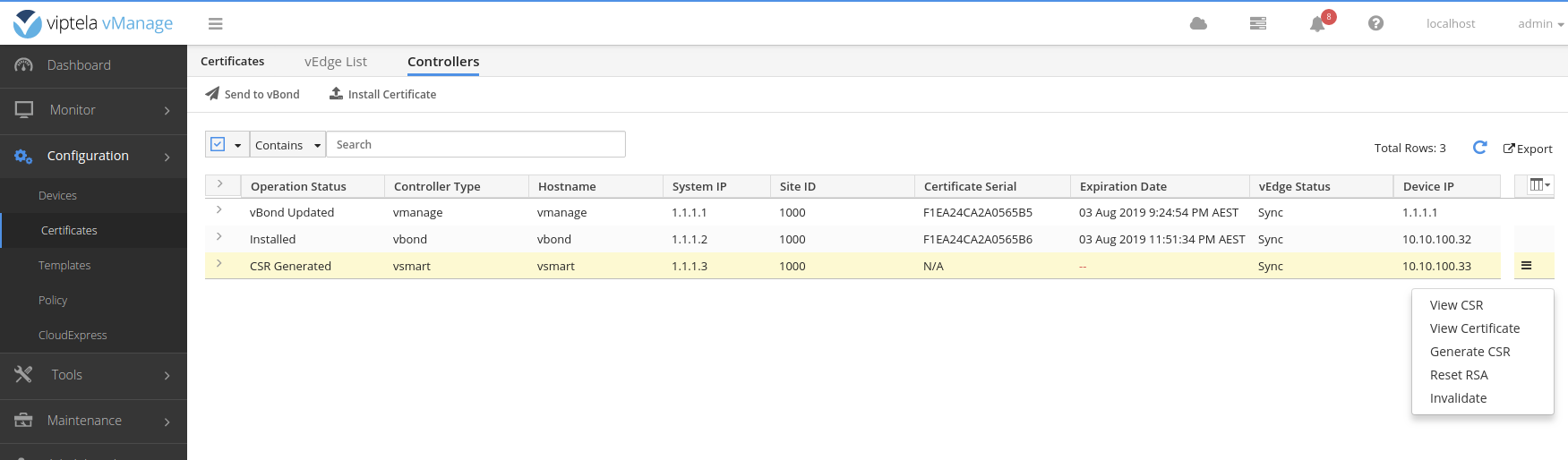
A window will popup with the CSR text. In the vshell on the vManage use vim to create a file named vsmart.csr with the text from the popup.
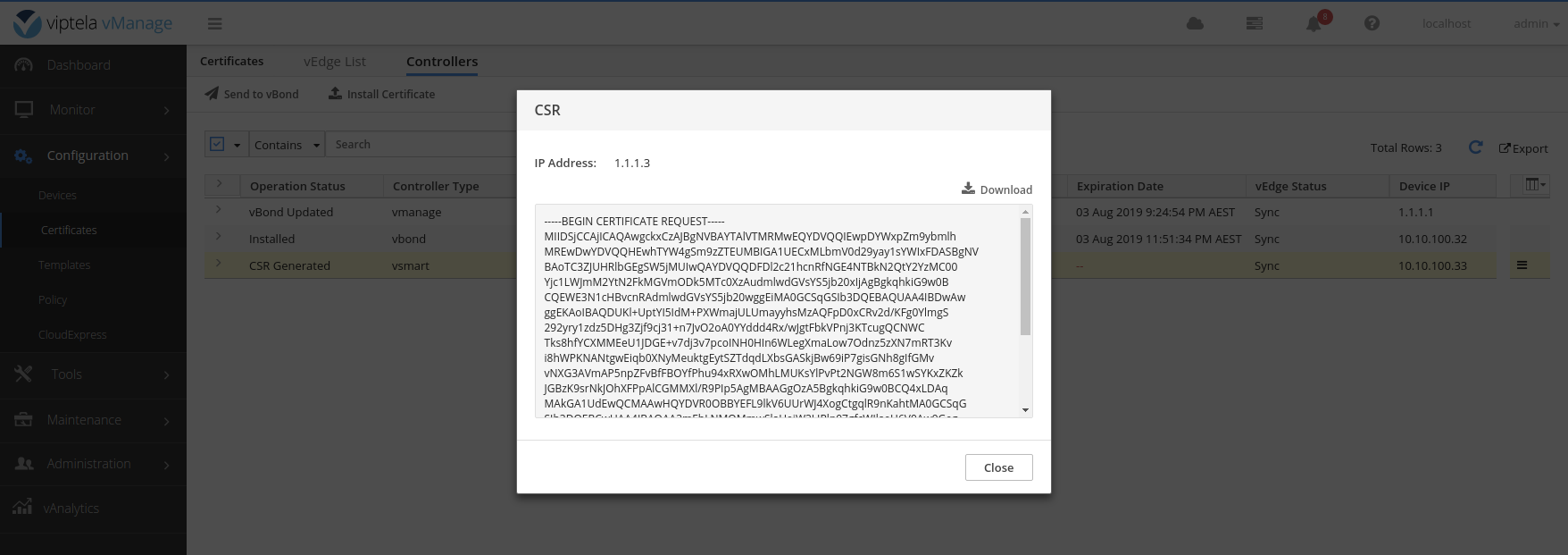
On the vManage sign the vsmart.csr file with the ROOTCA.key
# vshell
openssl x509 -req -in vsmart.csr \
-CA ROOTCA.pem -CAkey ROOTCA.key -CAcreateserial \
-out vsmart.crt -days 500 -sha256
# output
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=San Jose/OU=network-lab/O=vIPtela Inc/CN=vsmart_4a850d7d-cf30-4b75-bf3f-7ad0ef899174_0.viptela.com/emailAddress=support@viptela.com
Getting CA Private KeyUse the cat command to view the contents of the vsmart.crt file and install the certificate in the web interface.
Paste the contents into the popup
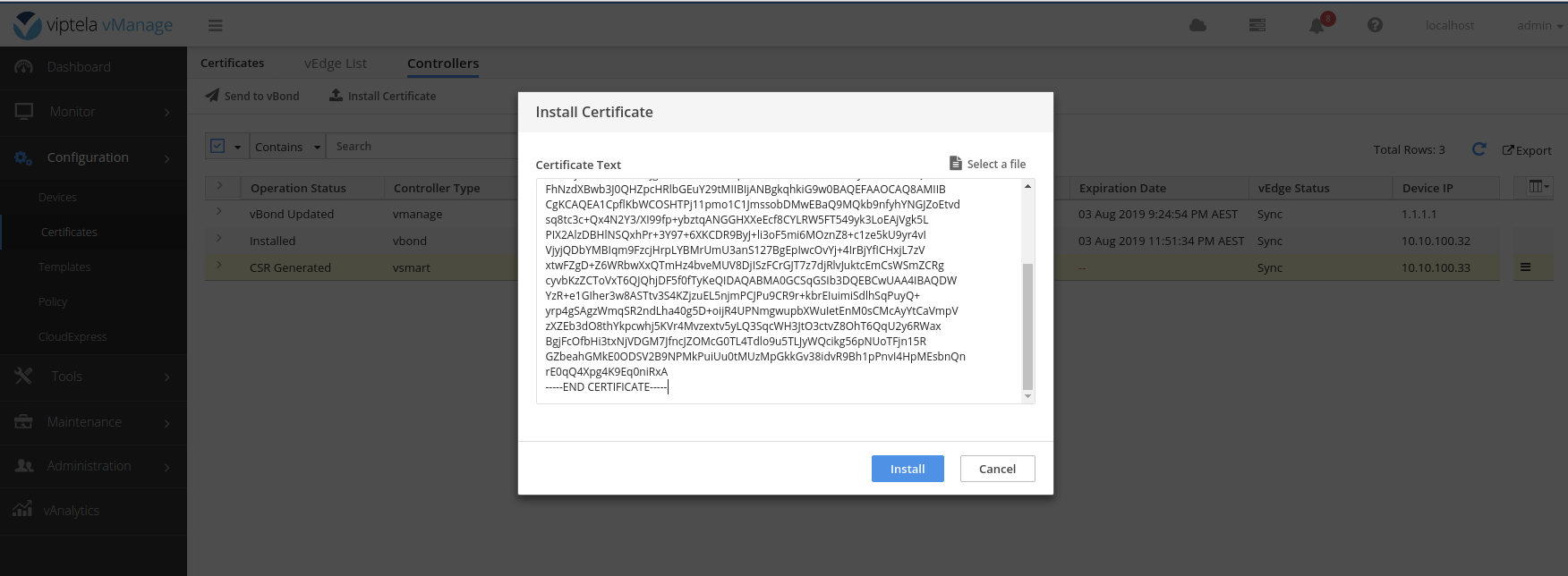
Sample successful certificate install log
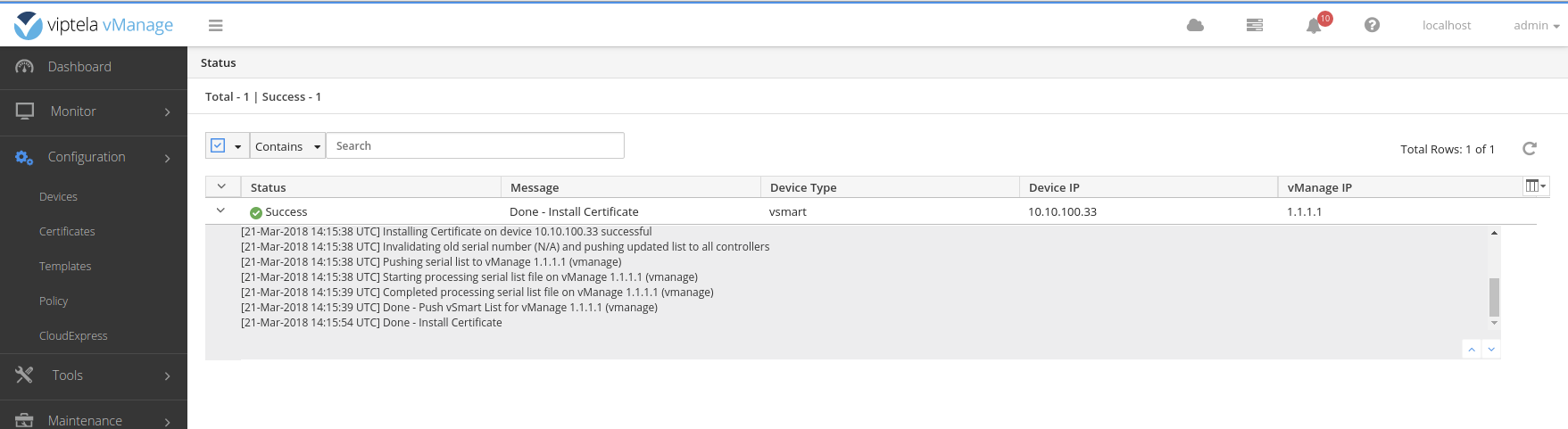
No need to update the vBond this time as the vBond was updated as part of the certificate install.
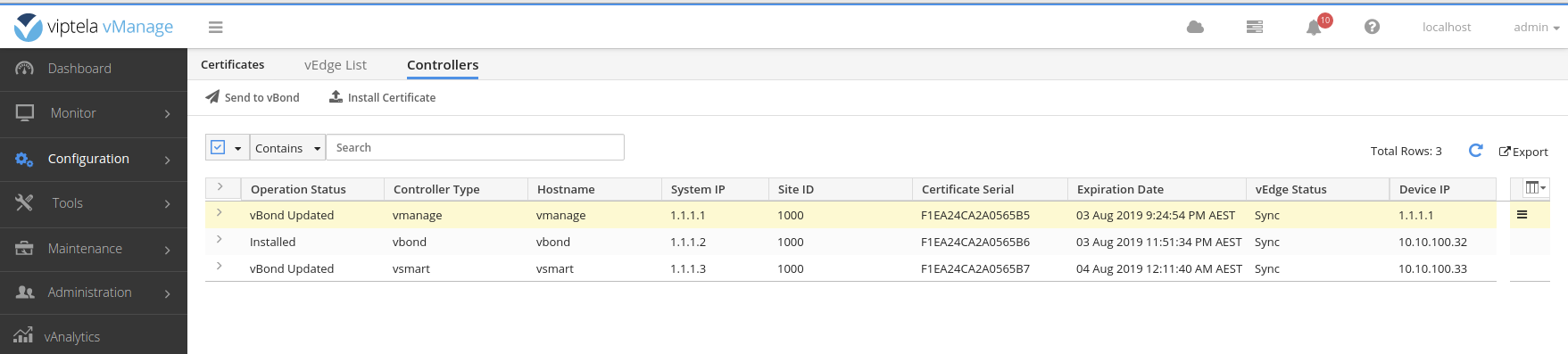
Finally, on the vSmart install the vsmart.crt certificate
# viptela-cli
request certificate install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vsmart.crt vpn 512
# output
Installing certificate via VPN 512
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vsmart.crt via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
vsmart.crt 100% 1310 2.3MB/s 00:00
Successfully installed the certificatevEdge
Add the ROOTCA.pem certificate to the vEdge root certificate chain.
# viptela-cli
request root-cert-chain install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem vpn 512
# output
Uploading root-ca-cert-chain via VPN 512
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/ROOTCA.pem via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
ROOTCA.pem 100% 1269 2.5MB/s 00:00
Updating the root certificate chain..
Successfully installed the root certificate chainGenerate a certificate signing request. Ensure to enter the organization name as network-lab at the prompts.
# viptela-cli
request csr upload scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vedge-01.csr vpn 512
# output
Uploading CSR via VPN 512
Enter organization name : network-lab
Re-enter organization name : network-lab
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 413]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 413]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
Generating private/public pair and CSR for this vedge device
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 417]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 417]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
Generating CSR for this vedge device ........[DONE]
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vedge-01.csr via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
server.csr 100% 1216 3.4MB/s 00:00
CSR upload successfulOn the vManage have the vedge-01.csr signed.
# vshell
openssl x509 -req -in vedge-01.csr \
-CA ROOTCA.pem -CAkey ROOTCA.key -CAcreateserial \
-out vedge-01.crt -days 500 -sha256
# output
Signature ok
subject=/C=US/ST=California/L=San Jose/OU=network-lab/O=vIPtela Inc/CN=vedge-ea3feb44-7869-4d35-83fd-fb6e1e81c3f1-0.viptela.com/emailAddress=support@viptela.com
Getting CA Private KeyBack on the vEdge install the signed certificate.
# viptela-cli
request certificate install scp://admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vedge-01.crt vpn 512
# output
Copying ... admin@172.16.100.31:/home/admin/vedge-01.crt via VPN 512
Warning: Permanently added '172.16.100.31' (ECDSA) to the list of known hosts.
viptela 16.3.2
admin@172.16.100.31s password:
vedge-01.crt 100% 1310 2.7MB/s 00:00
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 423]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 423]
CMD_MAAPI is true [mtid = 0]
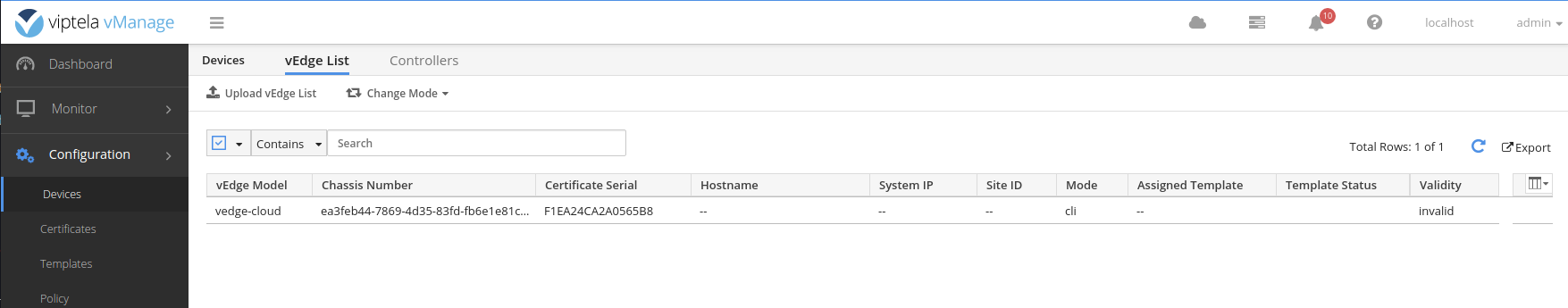
Successfully installed the certificateGet the certificate details from the vEdge.
# viptela-cli
show certificate serial
# output
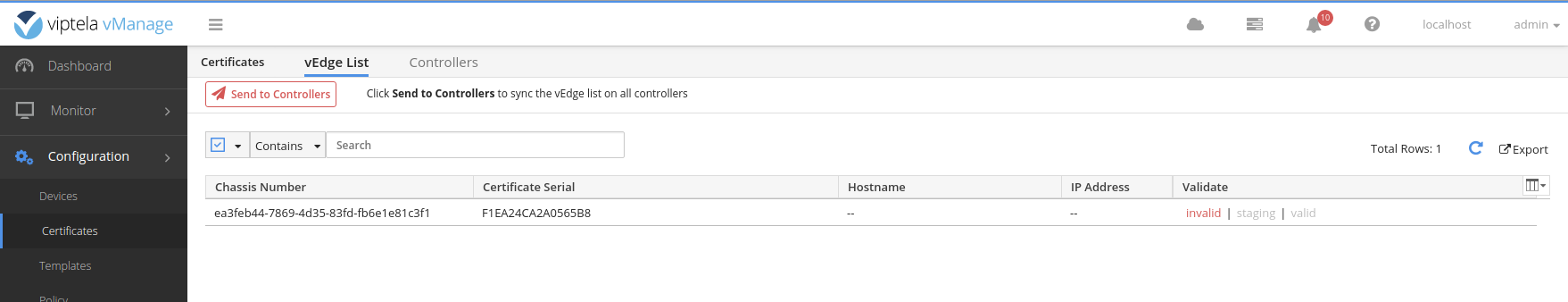
Chassis number: ea3feb44-7869-4d35-83fd-fb6e1e81c3f1 serial number: F1EA24CA2A0565B8A vEdge serial file needs to be uploaded to the vManage to ensure only authorized vEdges can connect to the fabric. Prior to software version 17.x this file was just a CSV file made up of the chassis number and certificate serial number of the vEdges. After 17.x the vEdge serial file became a signed binary file that can only be downloaded from Viptela and only includes the vEdges for which you have purchased a license.
This is the reason we start by installing the vManage, vBond and vSmart on software version 16.3.2 and later upgrade to 17.2.0 after the vEdges are added to the control plane.
Create a file called vedges.csv and upload it to the vManage. A sample file contents is below.
ea3feb44-7869-4d35-83fd-fb6e1e81c3f1,F1EA24CA2A0565B8Repeat these steps for the desired number of vEdges you need in your topology.
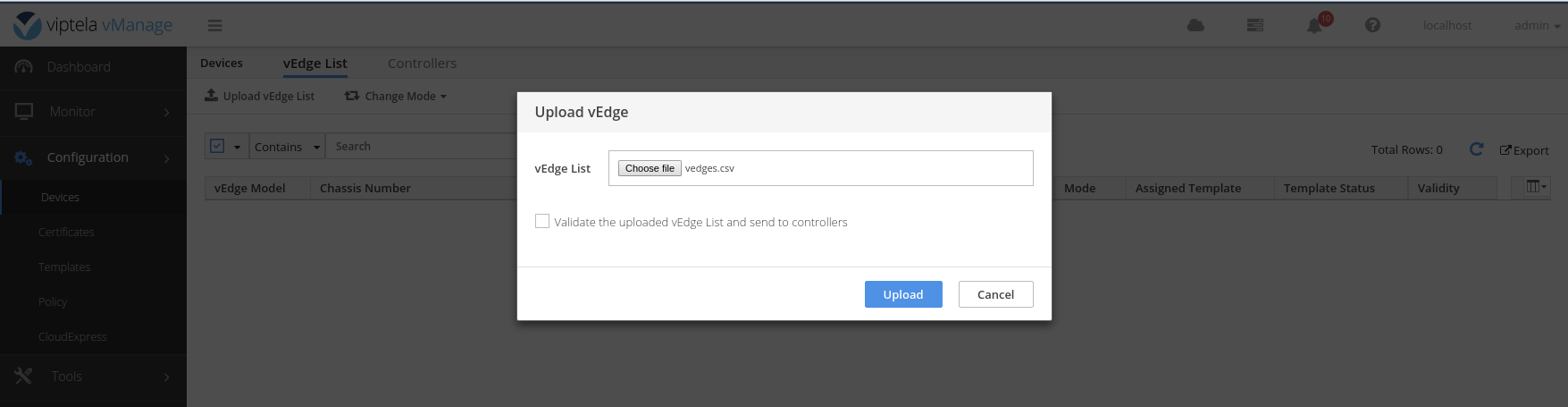
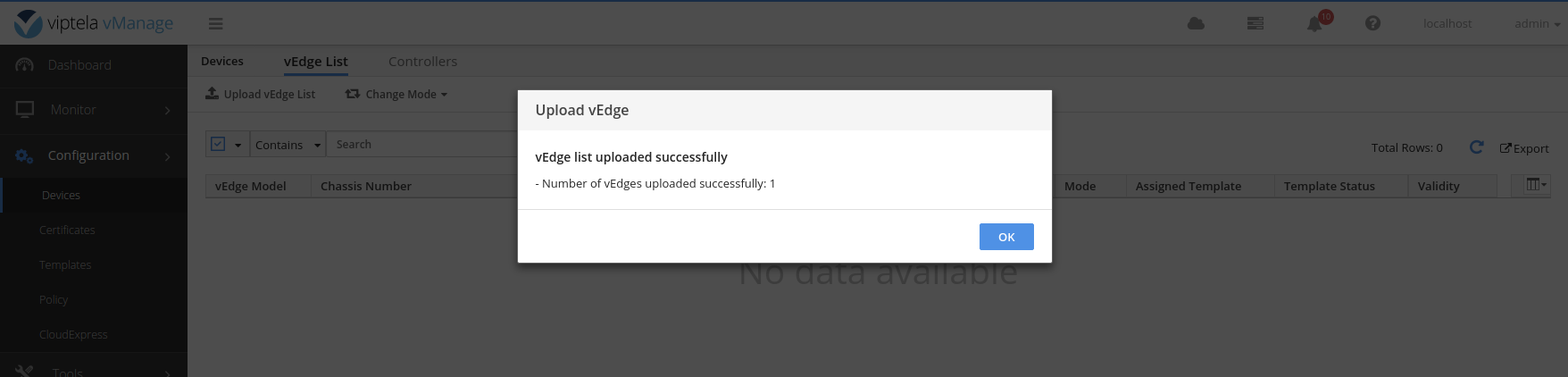
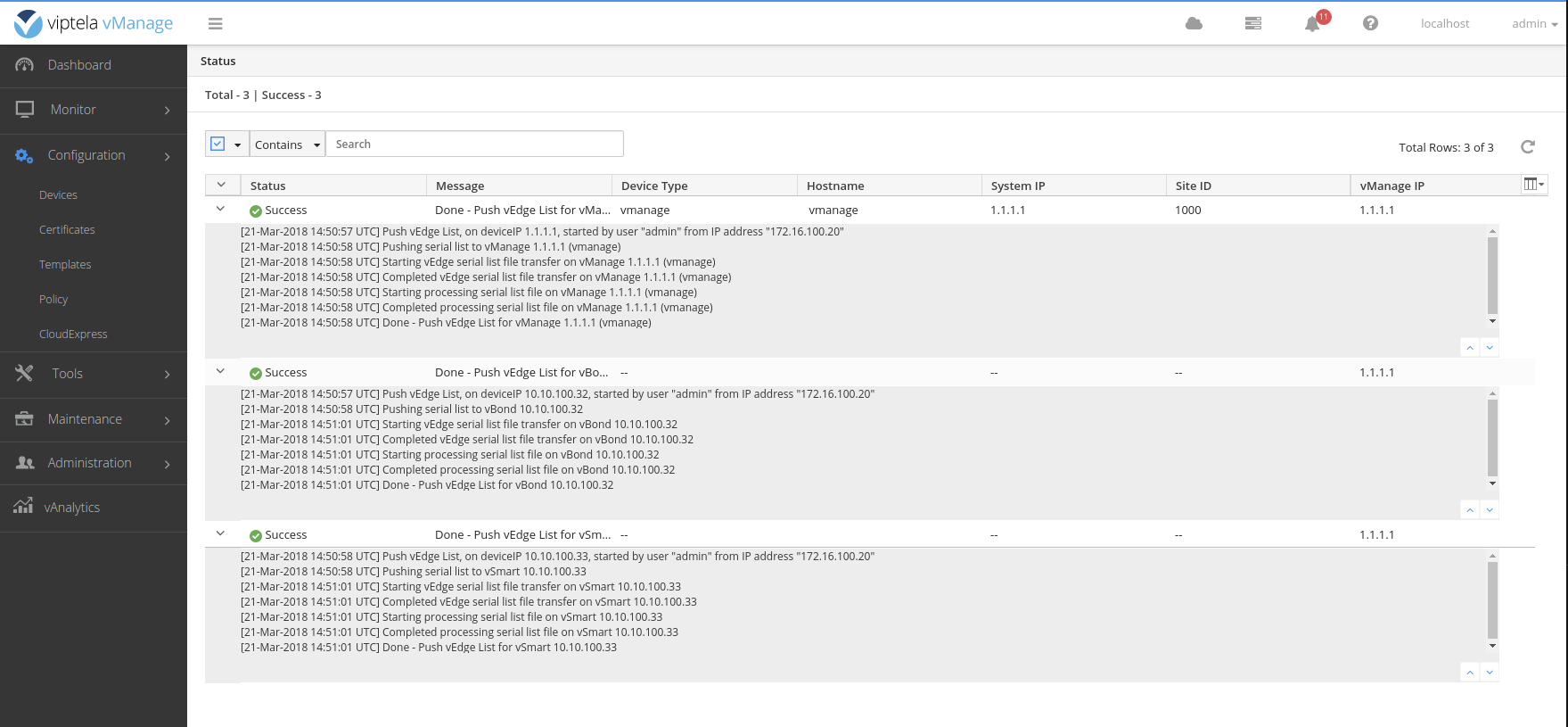
Send the list of vEdges to the controllers.
Tunnel Interfaces
The next step is to enable the tunnel interfaces on the vManage/Bond/Smart to bring up the control plane.
vManage/Smart
# viptela-cli
vpn 0
interface eth1
tunnel-interface
!vBond
# viptela-cli
vpn 0
interface ge0/0
tunnel-interface encapsulation ipsec
!Verification
There are a number of CLI commands that can be used to verify control plane status.
- show control local-properties
- Verify certificate installation status
- show control connections-history
- See why a control connection is failing
- show control connections
- Status of any current control connections
vManage
# viptela-cli
show control connections
# output
PEER PEER PEER SITE DOMAIN PEER PRIV PEER PUB
INDEX TYPE PROT SYSTEM IP ID ID PRIVATE IP PORT PUBLIC IP PORT REMOTE COLOR STATE UPTIME
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 vsmart dtls 1.1.1.3 1000 1 10.10.100.33 12346 10.10.100.33 12346 default up 0:00:02:42
0 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
1 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
2 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
3 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
4 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
5 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
6 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36
7 vbond dtls 1.1.1.2 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:06:36vBond
# viptela-cli
show orchestrator connections
# output
PEER PEER PEER SITE DOMAIN PEER PRIVATE PEER PUBLIC
TYPE PROTOCOL SYSTEM IP ID ID PRIVATE IP PORT PUBLIC IP PORT REMOTE COLOR STATE UPTIME
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
vsmart dtls 1.1.1.3 1000 1 10.10.100.33 12346 10.10.100.33 12346 default up 0:00:03:30
vsmart dtls 1.1.1.3 1000 1 10.10.100.33 12446 10.10.100.33 12446 default up 0:00:03:29
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12346 10.10.100.31 12346 default up 0:00:07:15
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12446 10.10.100.31 12446 default up 0:00:07:15
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12546 10.10.100.31 12546 default up 0:00:07:16
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12646 10.10.100.31 12646 default up 0:00:07:15
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12746 10.10.100.31 12746 default up 0:00:07:15
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12846 10.10.100.31 12846 default up 0:00:07:16
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12946 10.10.100.31 12946 default up 0:00:07:16
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 13046 10.10.100.31 13046 default up 0:00:07:16vSmart
# viptela-cli
show control connections
# output
PEER PEER PEER SITE DOMAIN PEER PRIV PEER PUB
INDEX TYPE PROT SYSTEM IP ID ID PRIVATE IP PORT PUBLIC IP PORT REMOTE COLOR STATE UPTIME
--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
0 vbond dtls - 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:00:19
0 vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12346 10.10.100.31 12346 default up 0:00:00:10
1 vbond dtls - 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:00:00:18Software Upgrade
The software upgrade process is well documented on the Viptela support portal here so I will not go into very much detail apart from a few points.
Head over to https://docs.viptela.com/Downloads and download the release 17.2.0 for upgrades. You will only need the vEdge Cloud, vSmart, Software vBond and the vManage files.

Upload the files to the vManage file repository.
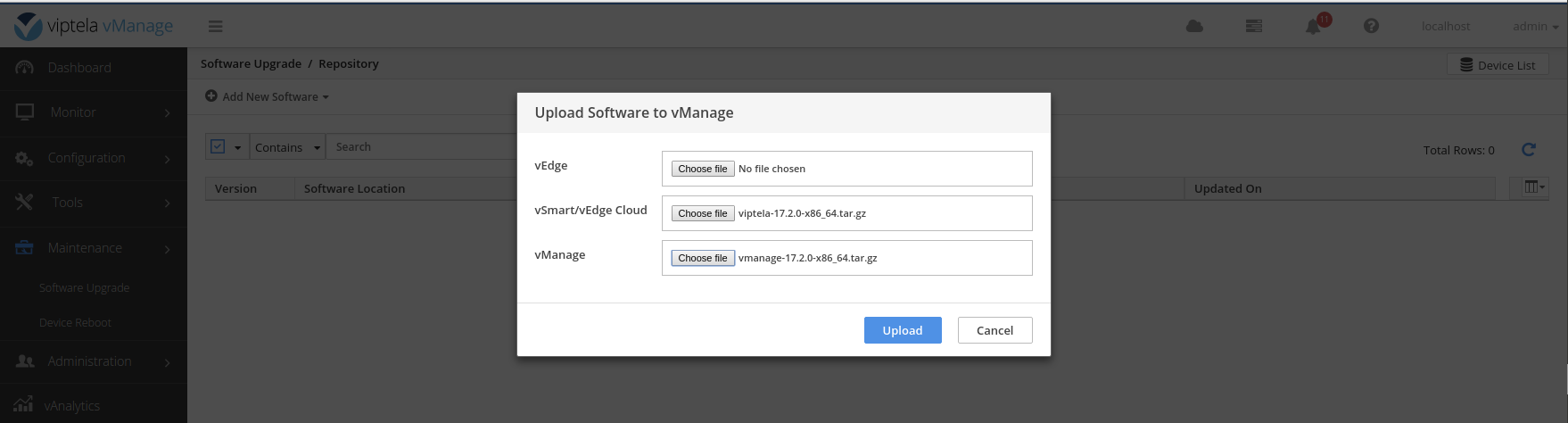
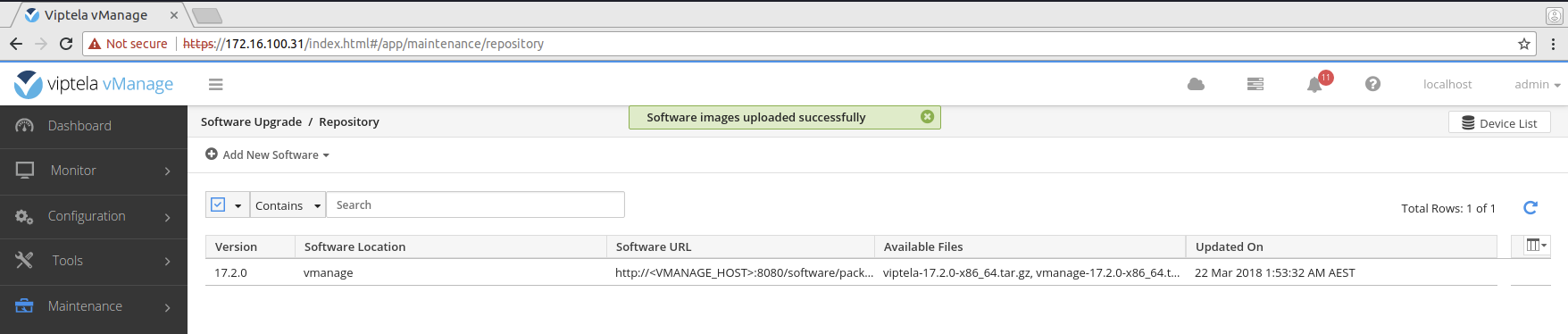
vManage
Load the software on the vManage.
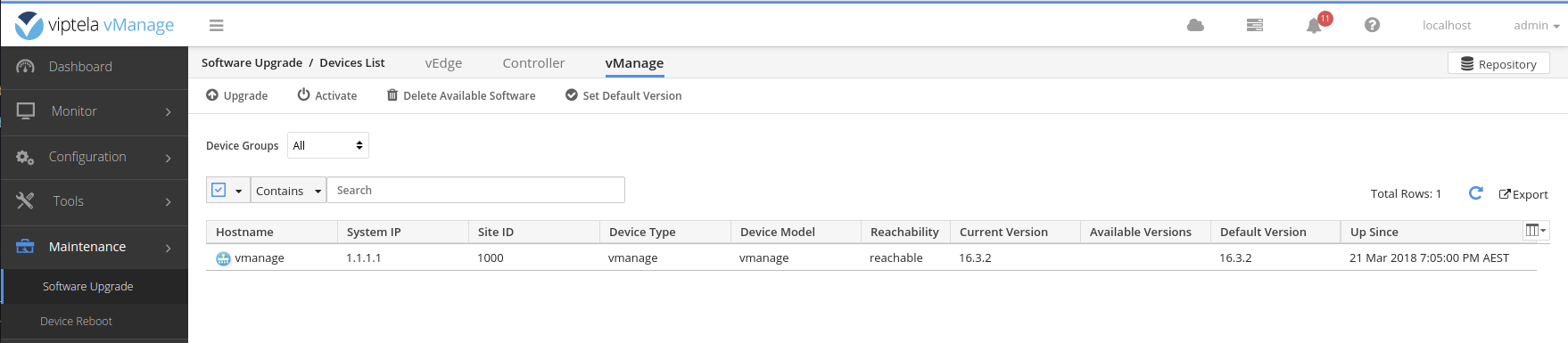
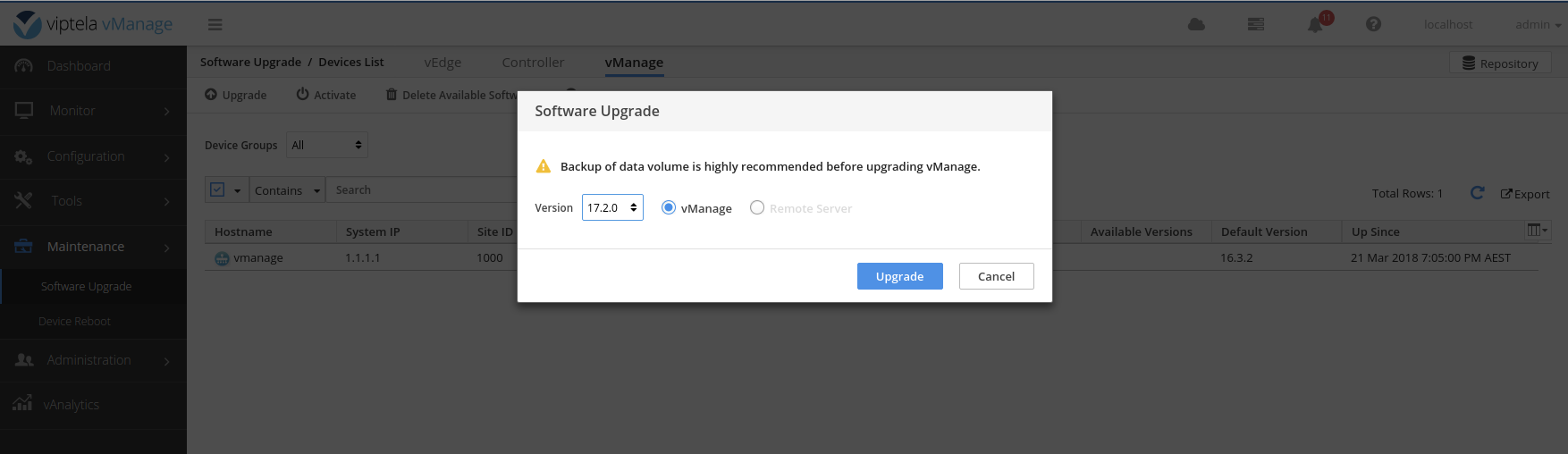
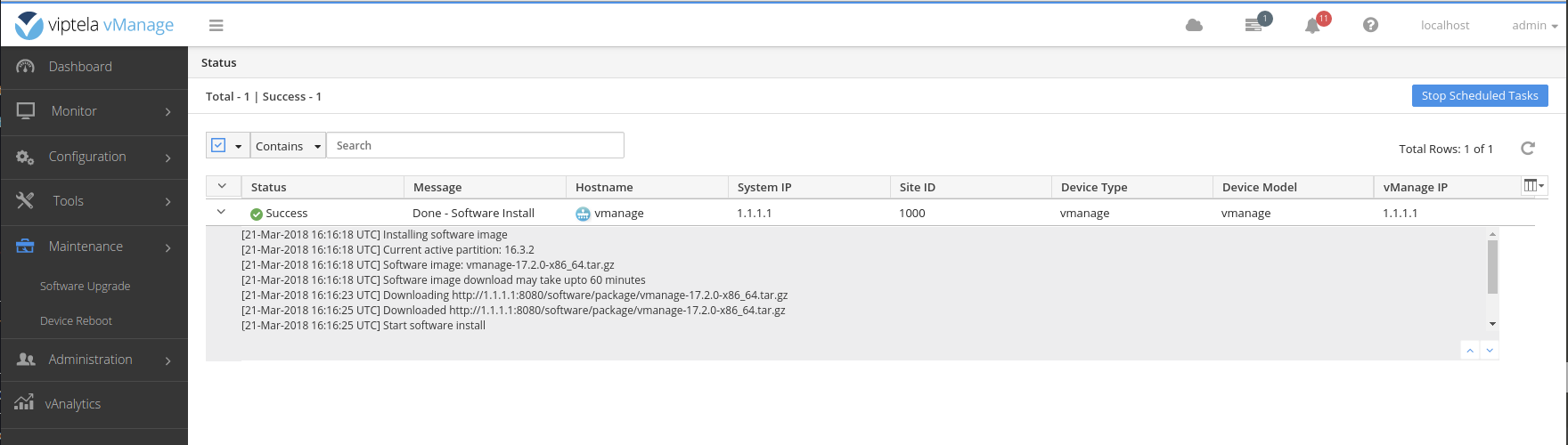
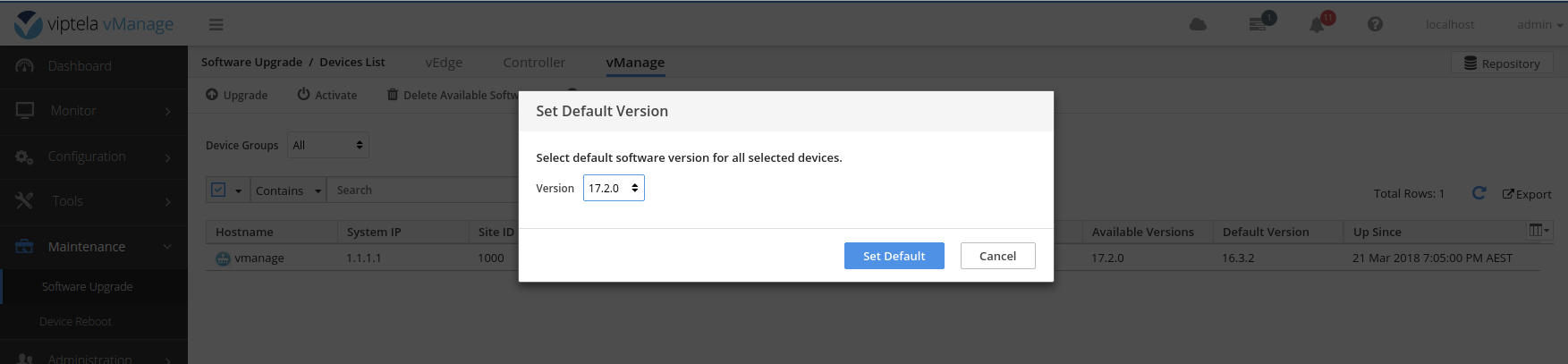
Set the default software version on the vManage.
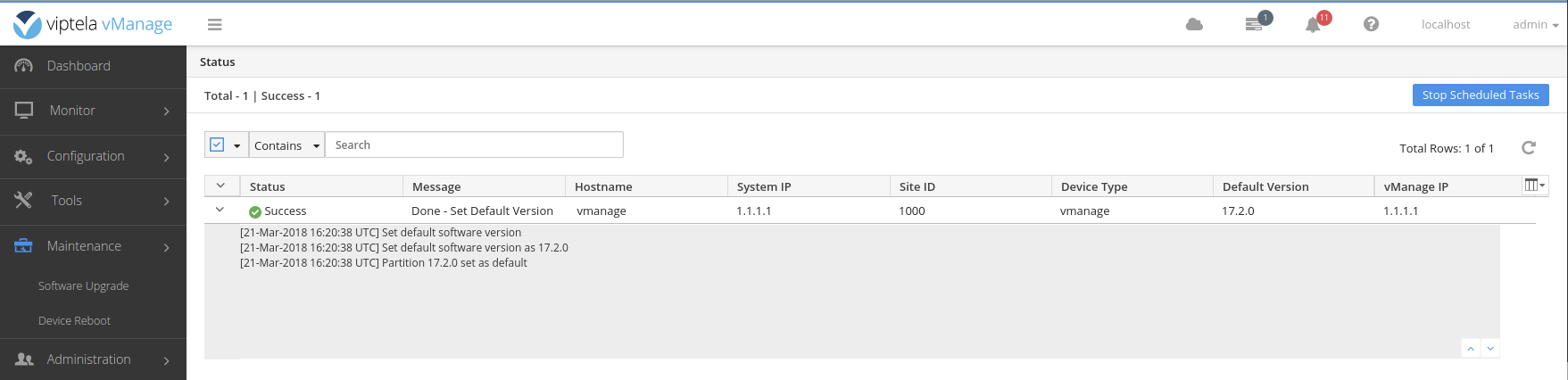
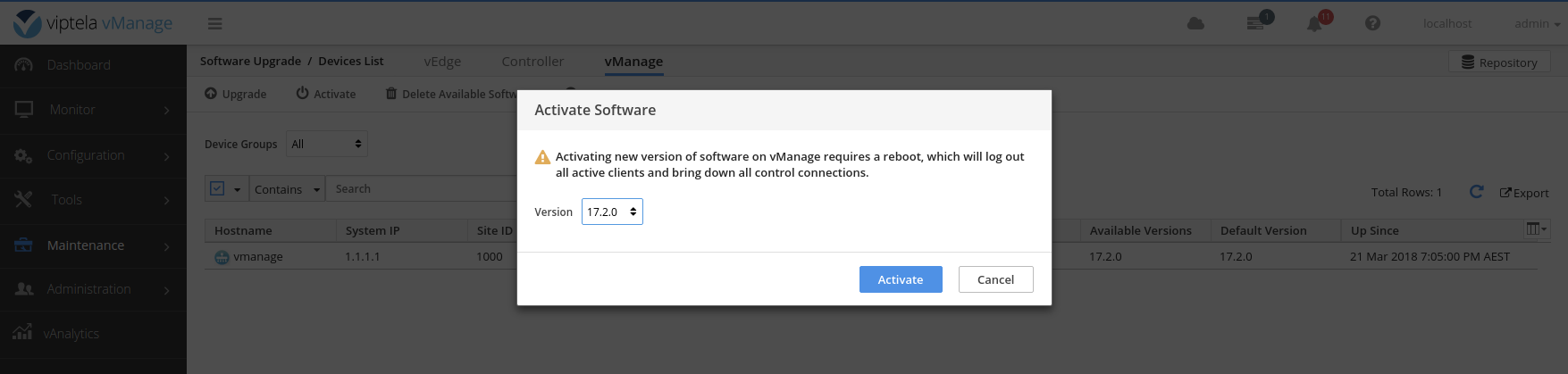
Activate the new software version on the vManage.
vBond/Smart
Load the software on the vBond/Smart, this can be done simultaneously for both devices.
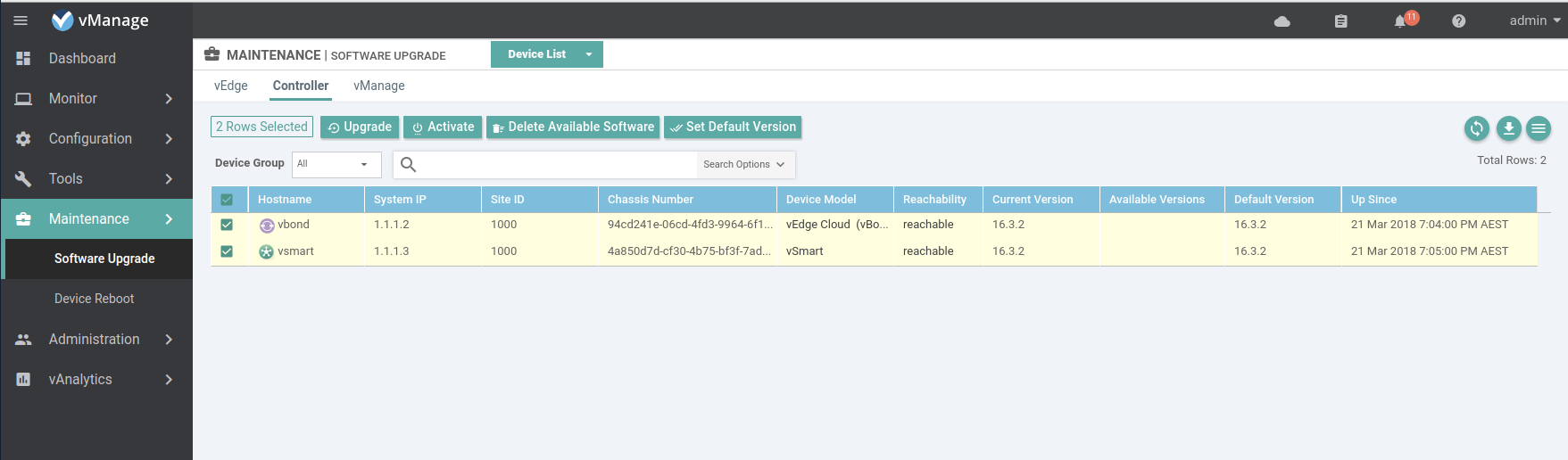
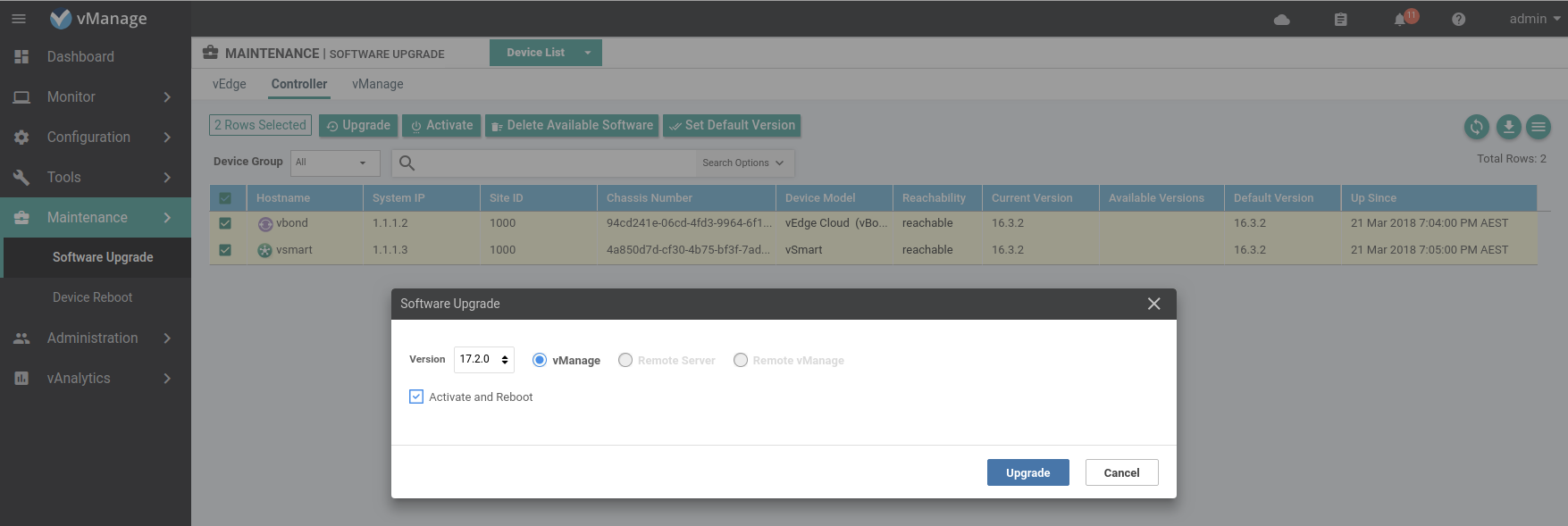
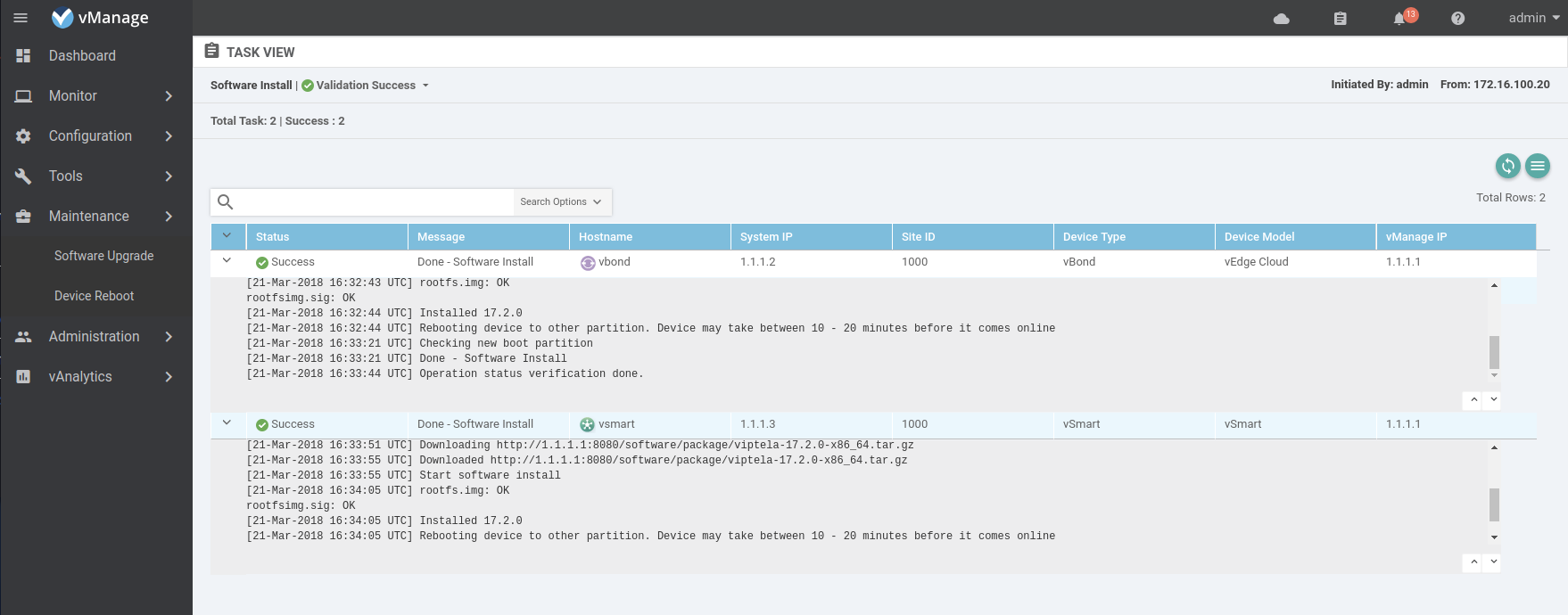
Set the default software version on the vBond/Smart.
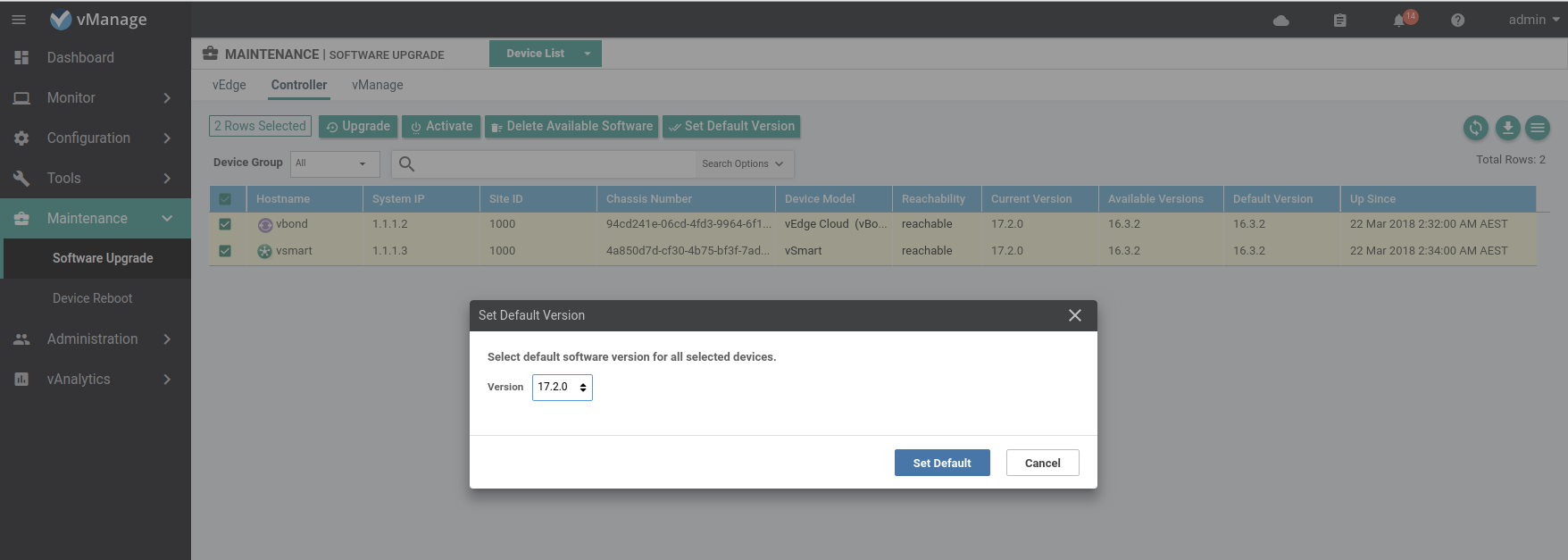
Validate vEdges
Now that the controllers are all upgraded to software version 17.2.0 it is safe to validate the vEdges so they can join the control plane.
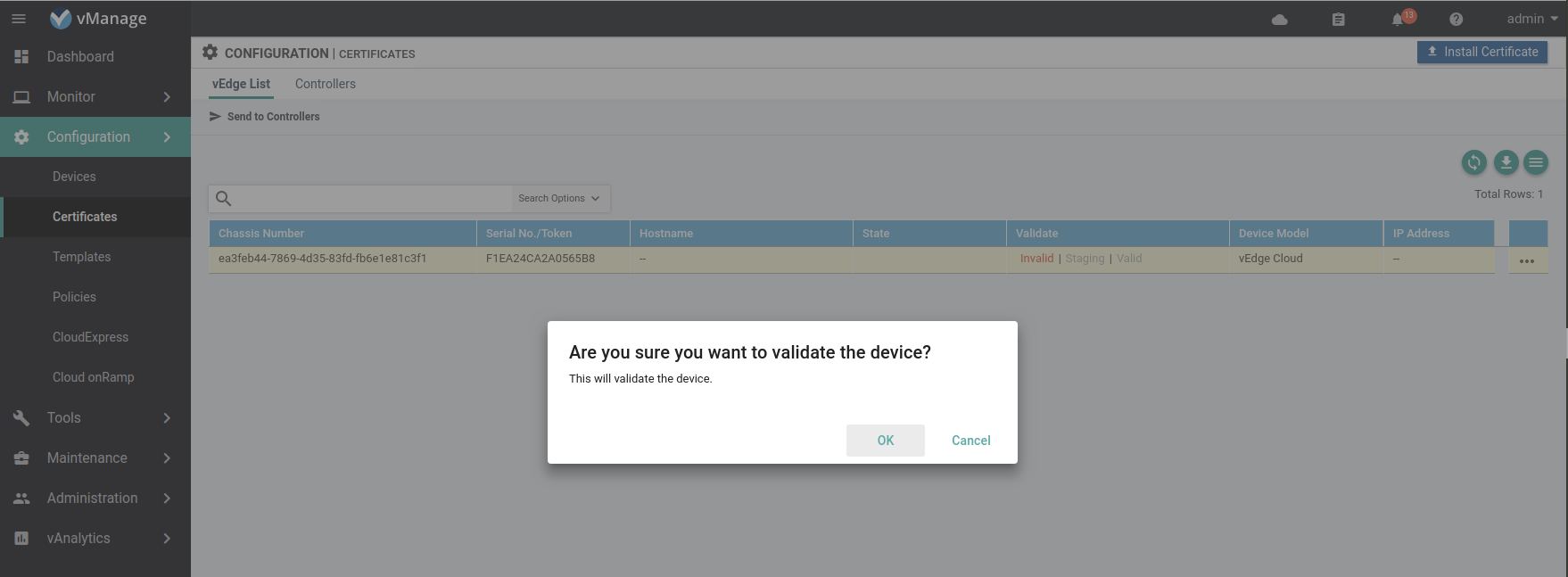
Now send the list of vEdges to the other controllers.

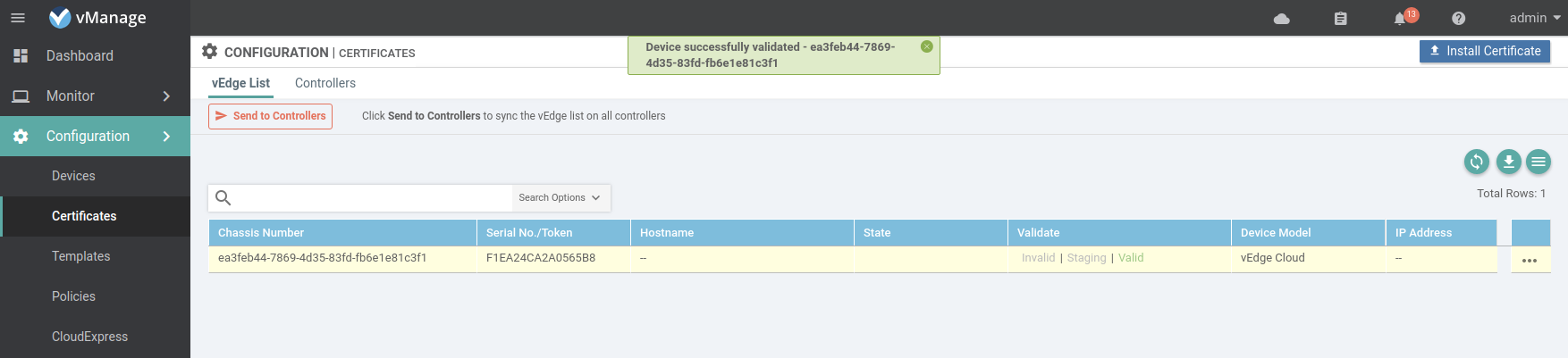
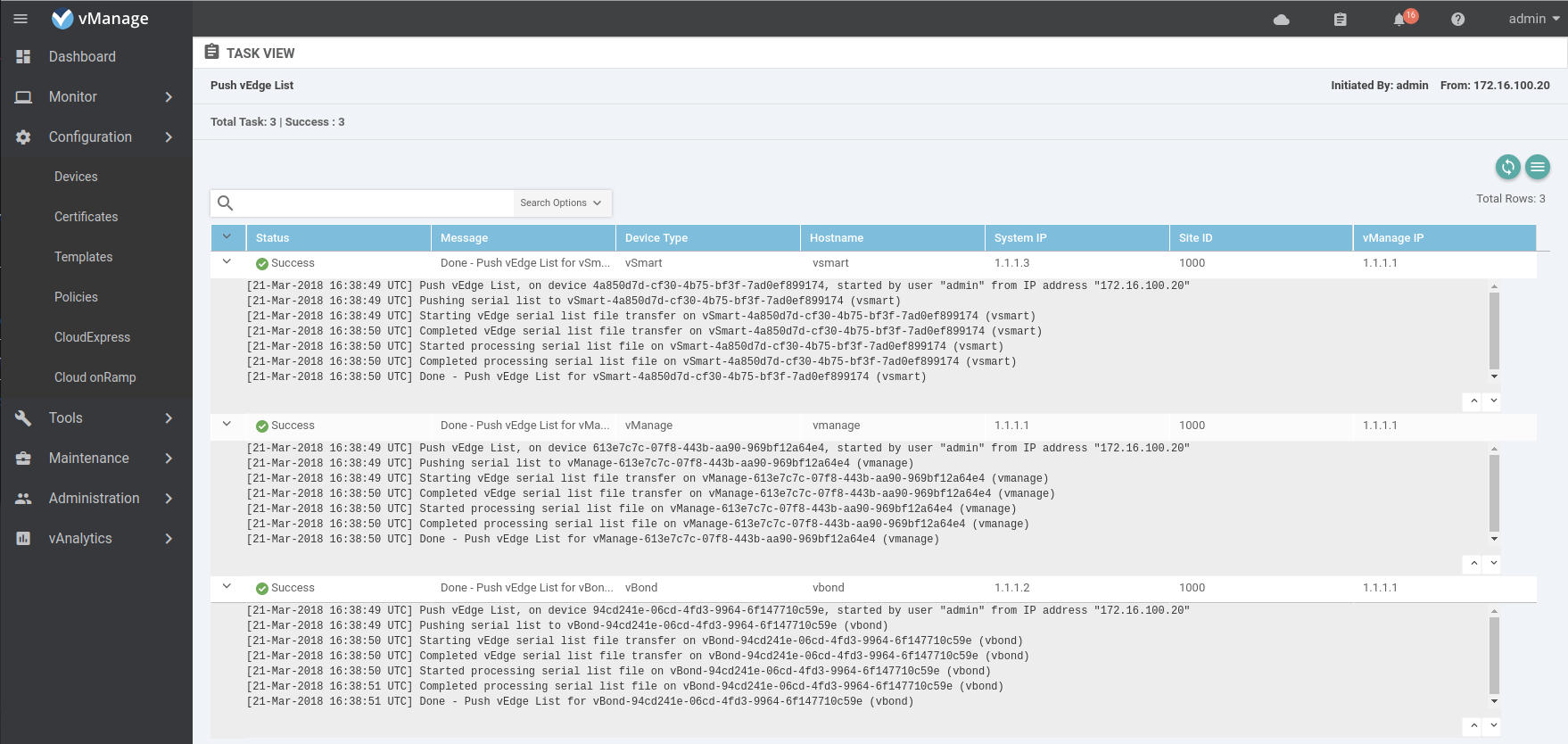
Once the vEdge list is pushed to the controllers the vEdges will start to join the control plane. You can verify the status by checking the devices list in the vManage web interface or checking the control connection on the vEdge.
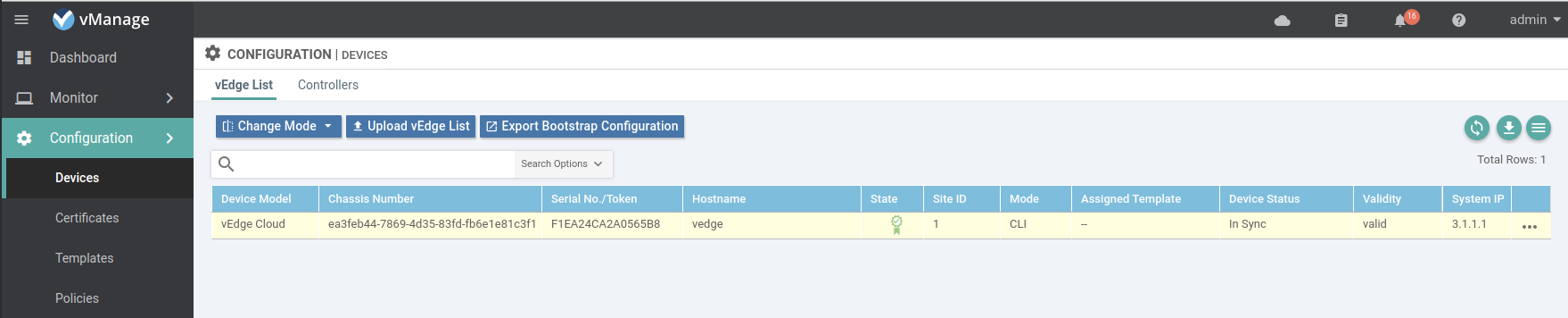
# viptela-cli
show control connections
# output
PEER PEER PEER SITE DOMAIN PEER PRIV PEER PUB GROUP
TYPE PROT SYSTEM IP ID ID PRIVATE IP PORT PUBLIC IP PORT LOCAL COLOR STATE UPTIME ID
----------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
vsmart dtls 1.1.1.3 1000 1 10.10.100.33 12346 10.10.100.33 12346 default up 0:08:43:33 0
vbond dtls - 0 0 10.10.100.32 12346 10.10.100.32 12346 default up 0:08:43:33 0
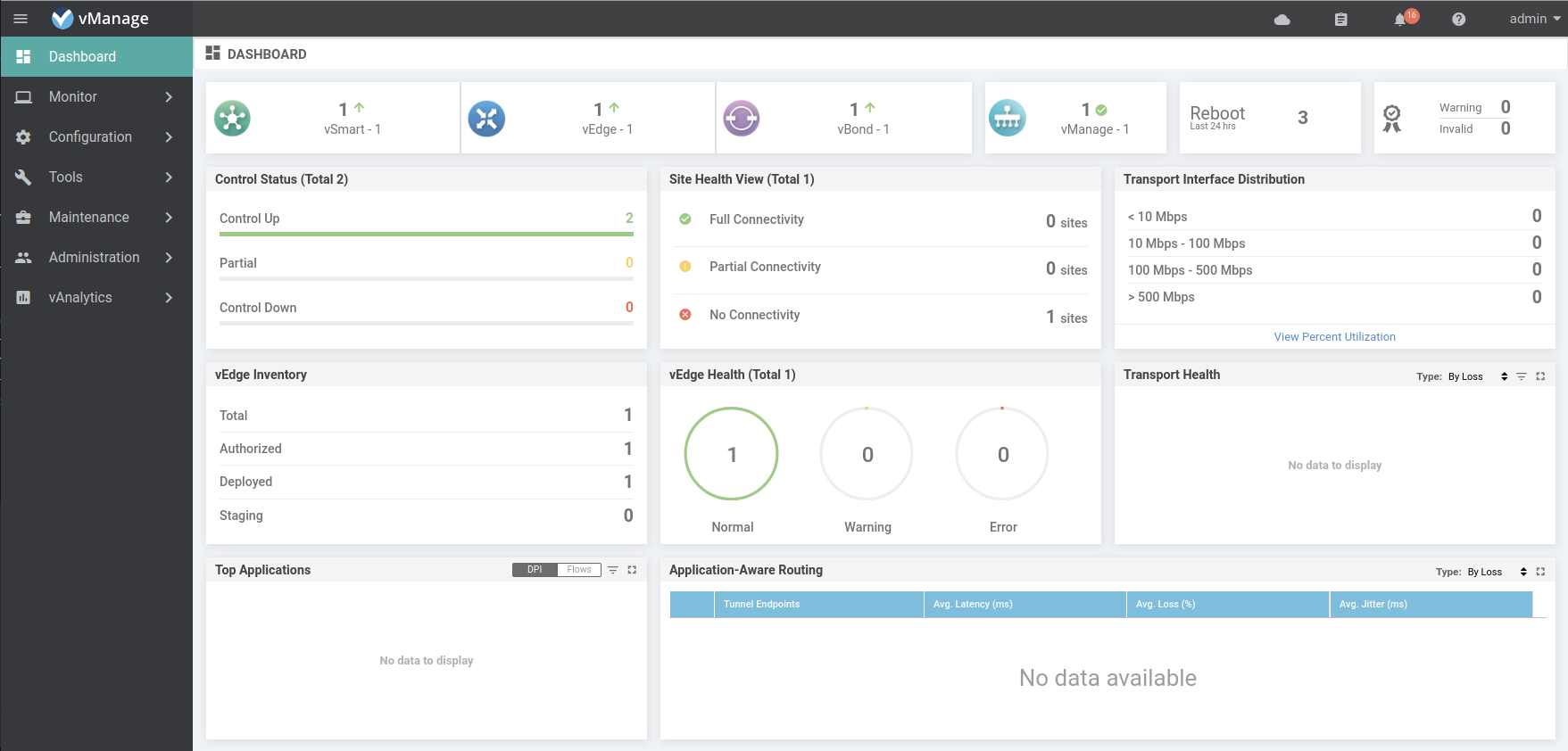
vmanage dtls 1.1.1.1 1000 0 10.10.100.31 12346 10.10.100.31 12346 default up 0:08:43:33 0View the dashboard to see the status of the Viptela platform.
Snapshot VMs
At this point I usually take a snapshot of the VM's so that you can quickly build out a topology starting with X number of vEdges connected to the controllers without having to going through this process every time. I will leave this as an exercise for the reader to investigate if that is something you wish to pursue.
Outro
If you made it this far you should have a Viptela lab up and running with a functioning control plane using your own self signed certificates and X number of virtual vEdges validated and ready to receive policy.