Cloud Notes: AWS EC2
published: 13th of March 2023
Intro
AWS Elastic Compute Cloud is an on-demand virtual machine based service. Virtual machines are available in many flavours of Operating System (OS), as well as multiple options for CPU types and high performance networking.
Elastic Network interface
Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) are virtual network cards that are attached to EC2 instances. ENIs have the following charactersitics.
- Each EC2 instance has a Primary ENI that cannot be removed from the instance or transferred to another instance. Additionaly, the interface is automaticlaly deleted when the instance is deleted.
- Additional Secondary ENIs can be added to an EC2 instance, however, the interfaces must reside in the same Availability Zone (AZ) as the instance.
- Secondary interfaces can be detached from an instance and moved to another instance. However, the other instance must be in the same AZ.
- Secondary intrfaces can reside in a different Subnet from the Primary interface as long as it is in the same AZ.
- Each interface has it own Security Group associations.
- ENIs are assigned a Primary IPv4 and/or IPv6 address which is associated to the interface for the life of the instance.
- ENIs can optionally be assigned 1 or more Secondary IP addresses.
- Secondary IP addresses of the Primary ENI can be reassociated with another ENI.
- The MAC address, Primary/Secondary private IPv4 addresses, Elastic IP addresses (Public IPv4 addresses), IPv6 addresses, and Security Groups remain with a secondary network interface when it is detached from an instance.
- Enabling the auto-assign public IPv4 address setting for a Subnet will associate a Public IPv4 address to an ENI. However, this Public IPv4 address is not static. If the instance is Stopped or Restarted a new Public IPv4 address will be associated to the ENI.
- Public IPv4 addresses are not configured in the operating system of an EC2 instance. The Public IPv4 address is used at the Internet Gateway when performing NAT for the instance, to/from the interent.
- In order for an instance or an ENI to have a Static Public IPv4 address association, an Elastic IP address Must be assigned.
- Allocated Elastic IPs have a cost if they are not associated with a running instance. Or, if the instance they are associated with is in the Stopped state.
- All IPv6 addresses are Publicly routable and IPv6 addresses associated with an ENI Are configured in the OS of the EC2 instance.
- The number of Secondary interface and Seconary IP addresses that can be associated is dependent on the Instance type.
- Source/destination checks are enabled by default and are used to confirm that the ENI is either the Source or Destination of traffic it processes. If it is not, the traffic is dropped.
- Source/destination checks are configued on a Per-ENI basis.
- Source/destination check is usually disabled on NAT, Proxy, Load Balancer, Firewall and Routed devices, since traffic will often enter one interface and exit another which is not part of the Source/Destination of the traffic flow.
Enhanced Networking
EC2 instances by default are provisioned with Elastic Network Interfaces (ENIs) that have limited performace.
Enhanced Netowking utilzes Single Root I/O Virtualization (SR-IOV) to provide high-performance networking capabilities on supported EC2 instance types.
SR-IOV provides higher I/O performance, higher bandwidth, higher Packets Per-Second (PPS) and lower CPU utilization compared to the default ENIs.
SR-IOV has the following characteristics.
- SR-IOV allows a single physical Peripheral Component Interconnect Express (PCIe) root port to appear as multiple seperate physical devices to a hypervisor or guest operating system.
- SR-IOV traffic bypasses the hypervisor's software switch, giving VMs near native network performance.
- SR-IOV uses Physical Functions (PFs) and Virtual Functions (VFs).
- PFs are full PCIe functions that are capable of configuring and managing the SR-IOV functionality. They also have the ability to move data in and out of the device.
- VFs are lightweight PCIe functions that support data flow but have a restricted set of configuration resources.
- The number of possible VFs is dependent on the device and can be up to 256.
Intel 82599 Virtual Function (VF) Interface
The Intel 82599 VF has the following characteristics.
- 82599 VF has support for up to 10 Gbps speeds.
- 82599 VF enhanced networking is enabled in the OS with the ixgbevf module driver.
- 82599 VF enhanced networking is enabled on an EC2 Instance by setting the sriovNetSupport attribute to simple.
- Many modern AMI images have the required modules pre-installed.
- HVM instances have 82599 VF enhanced networking enabled by default.
Elastic Network Adapter (ENA)
The ENA has the following characteristics.
- ENA has support for up to 100 Gbps speeds.
- ENA enhanced networking is enabled in the OS with the ena module driver.
- ENA enhanced networking is enabled on an EC2 Instance by setting the enaSupport attribute to true.
- Many modern AMI images have the required modules pre-installed and ENA support enabled by default.
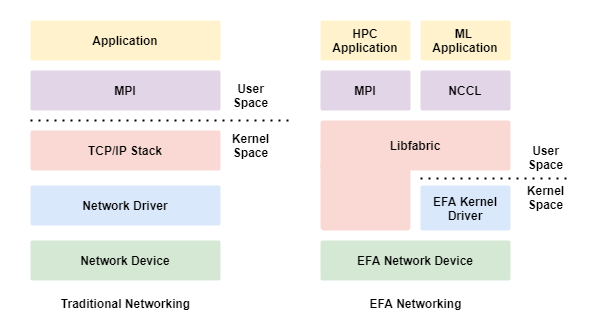
Elastic Fabric Adapter (EFA)
An EFA provides all the functionality of an ENA with additional OS-bypass capabilities.
The EFA has the following characteristics.
- OS-bypass allows HPC and Machine Learning workloads to communicate directly with the network iterface and achieve low-latency and high-reliability.
- With EFA, applications use MPI or NCCL to interface with the Libfabric API and bypass the operating systems TCP/IP stack.
- OS-bypass is only supported between noted in the same Subnet.
- Inter-Subnet traffic uses the OS's TCP/IP stack.
- OS-bypass traffic cannot be routed.
- A Security Group with a Self-Referential, Allow ALl IN/OUT, rule must be applied to instances using OS-bypass.
The following diagram show a traditional vs EFA networking stack.
Network Performance Considerations
Regardless of potential Network Adapter speeds, the following points should be considered about Network Performance in AWS.
- Inter-Region bandwidth has an aggregate quota of 5 Gbps.
- Within a region, a sigle flow (identified by a 5-tuple match) is limited to 5 Gbps.
- Multi-part upload for S3 or applications that use Multi-Path TCP are examples of options to get around the single flow 5 Gbps limit within a Region.
Placement Group
With Placement Groups, you can influence where a group of dependent instances are physically hosted. This allows you to appropriately position your workloads for various low latency, high throughput and redundancy scenarios.
There are 3 types of Placement Groups: Cluster, Spread and Partition.
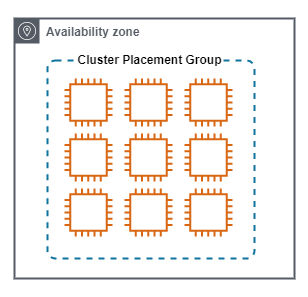
Cluster
A Cluster Placement Group, places instances close together.
Cluster Placement Groups have the following characteristics.
- Used when the highest level of inter-group low latency and performance is required. All members in the same groups, have fast and direct access to all other members.
- Performance between cluster members is up to 10Gbps per stream.
- The achieve the maximum possible netowrk performance, enhanced networking must be enabled.
- Instances are launced in a single Availability Zone. Often in the same rack, and pontentially on the same host.
- Can span VPC peers, but this does have a negative impact on performace.
- Not all instance types are supported.
The following diagram show a Cluster Placement Group.
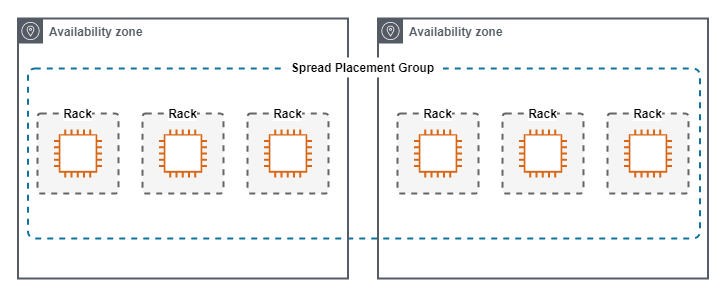
Spread
A Spread Placement Group, keeps single instances physically seperated.
Spread Placement Groups have the following characteristics.
- Used when a small number of instances need close physical proximity, but also require seperation into different failure domains.
- Each instance lives in a phyisically diverse rack from other instances in the group.
- Maximum of 7 Instances Per-AZ.
- Instances can span multiple Availability Zones.
The following diagram show a Spread Placement Group.
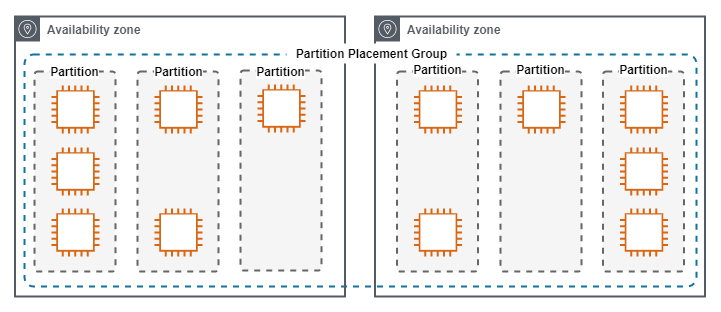
Partition
A Partition Placement Group, keeps groups of instances physically seperated.
Partition Placement Groups have the following characteristics.
- Used when a large number of instances need close physical proximity, but also require seperation into different failure domains.
- Suitable for applications that are topology aware such as HDFS, HBase and Cassandra.
- Maximum 7 Partitions Per-AZ.
- The number of Instances Per-Partition is configurable by the administrator and the maximum is dependent on the account limits.
- Instance groups placement can be auto-assigned by AWS or manually by the administrator.
- A partition placement group with Dedicated Instances can have a maximum of two partitions.
The following diagram show a Partition Placement Group.
Instance Metadata
EC2 instance metadata is data about the running EC2 instance and the AWS environment that can be queried from the instance.
- The instance metadata is accessible at http://169.254.168.254
- The most up to date metadata can be accessed at http://169.254.168.254/latest/meta-data
- Metadata is split into groups and be accessed by querying the relevant URI. For example: http://169.254.168.254/latest/meta-data/public-ipv4
- The metadata service is NOT encrypted and has NO authentication.
Links
https://learn.cantrill.io/courses/1231680
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-eni.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/MultipleIP.html
https://aws.amazon.com/premiumsupport/knowledge-center/secondary-private-ip-address/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/configure-subnets.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/vpc/latest/userguide/working-with-subnets.html#subnet-public-ip
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-instance-addressing.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/using-eni.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/enhanced-networking.html#supported_instances
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/instance-types.html#instance-type-summary-table
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/sriov-networking.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/enhanced-networking-ena.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/WindowsGuide/enhanced-networking.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/virtualization_types.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/efa.html
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/AWSEC2/latest/UserGuide/placement-groups.html
https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Forwarded-For
https://aws.amazon.com/blogs/aws/elastic-load-balancing-adds-support-for-proxy-protocol/