AWS Networking
updated: 7th of January 2024
published: 2nd of February 2023
Intro
Apparently, there is still networking in the cloud. Who would have thunk it? This post is a high level overview of the AWS networking infrastructure and services. As I skip along the path to obtaining the AWS Advanced Networking Speciality certification I will update this post, and will also link to other posts I create, where having more detailed information makes sense.
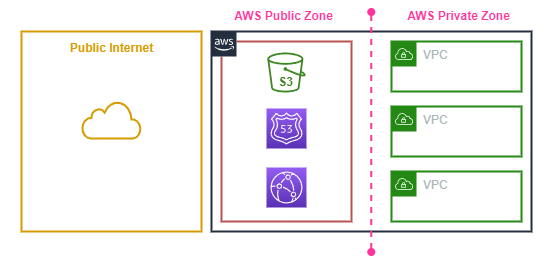
Public vs Private Zones
The AWS network is split up into two zones; the Public Zone and the Private Zone. Some AWS services such as S3 live in the Public zone which has access to and from the internet. Services in the Private Zone, by default have no access to or from the internet or other services in AWS.
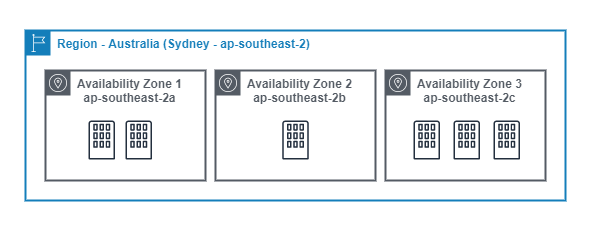
Region
A Region is a collection of physical data centres that are logically grouped in a regional cluster. An AWS region has a minimum of 3, isolated and physically seperate Availbility Zones (AZ).
The following diagram shows the ap-southeast-2 (Sydney) region.
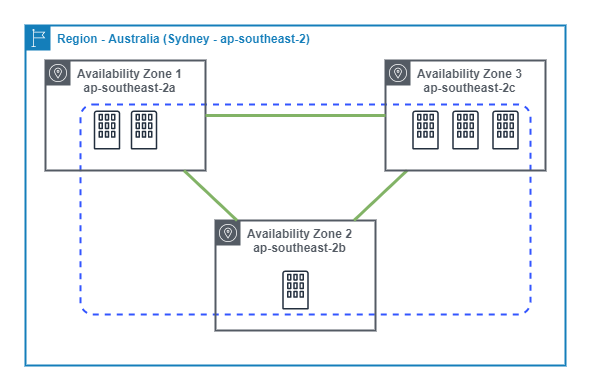
Availability Zone
An Availability Zone (AZ) is 1 (or more) physically isolated data centres with redundant power, networking and connectivity located within a Region.
AZs in a Region are seperated by many kilometres, but all are within a 100km radius of each other.
AZs are connected by high bandwidth, low-latency networking allowing for sychronous replication and high-availability applications. Additionally, all traffic between AZs is encrypted.
The following diagram show the ap-southeast-2 (Sydney) regions availability zones.
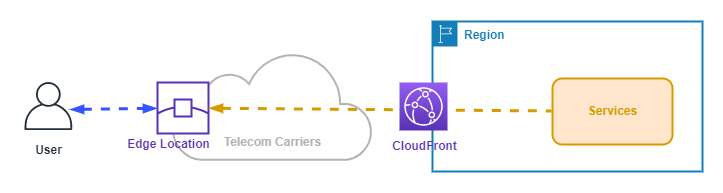
Edge Location
An Edge Location is a Point-of-Presence (PoP) that is located closer to end users than a Region. Edge locations peer with Telecom Carries via CloudFront to deliver low-latency access to some AWS services.
The following diagram shows an AWS Edge Location.
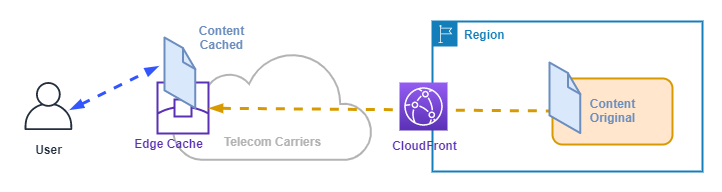
Edge Cache
An Edge Cache is a Regional PoP that is used to cache content close to the users via a CloudFront distribution.
The following diagram shows an AWS Edge Cache.
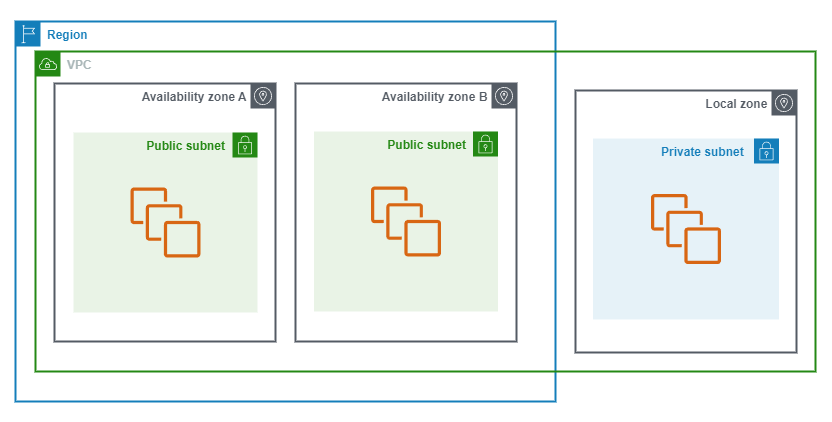
Local Zone
AWS Local Zones allow you to provide low-latency access users by extending an AWS region geographically closer to the users.
Local Zones place compute, storage, DB as well as other select AWS resources close to large population and industry centres.
Local Zones are only available in select Regions and locations.
The following diagram shows an AWS Local Zone.
Outpost
AWS Outposts allows you to extend and run native AWS services on premises. Outpost is AWS managed equiptment available in a variety of form factors from 1U and 2U Outposts servers to 42U Outposts racks, and multiple rack deployments.
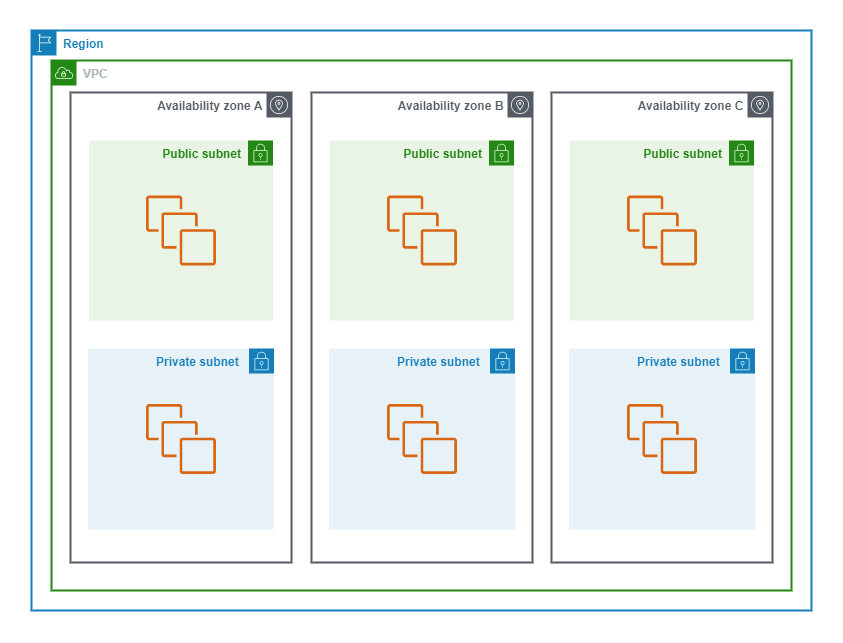
Virtual Private Cloud
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a logically isolated virtual network that by default, is segregated from other customers and the internet.
The following diagram shows an AWS VPC topology.
My notes on AWS VPCs can be found here.
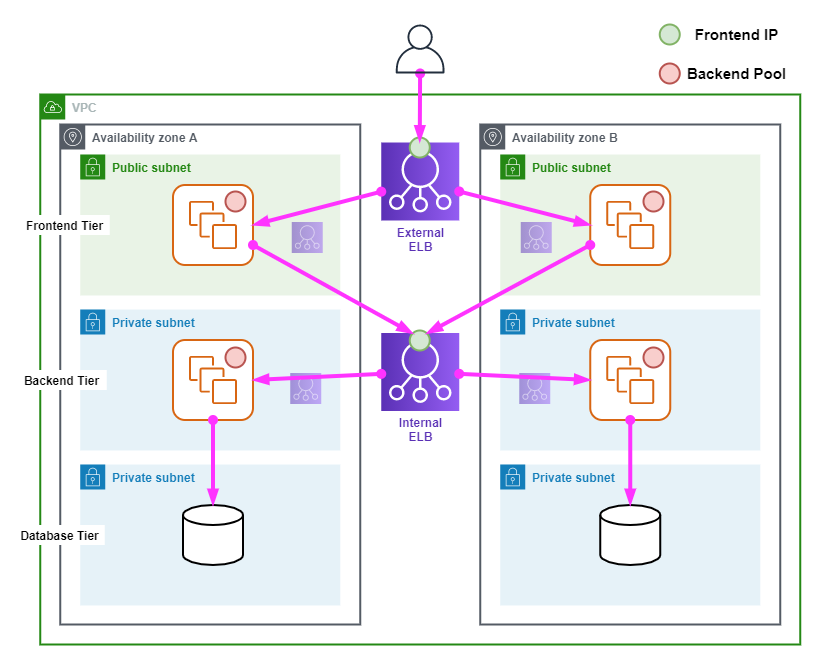
Elastic Load Balancing
Elastic load balancers (ELBs) allow you to horizontally scale a pool of backend servers and/or services behind a single frontend IP/Hostname.
The following diagram shows an AWS Elastic Load Balancing topology.
My notes on AWS ELBs can be found here.
Transit Gateway
Transit Gateway is a managed service that allows you to connect multiple VPCs and on-premises networks together.
The following diagram shows an example AWS Transit Gateway topology.
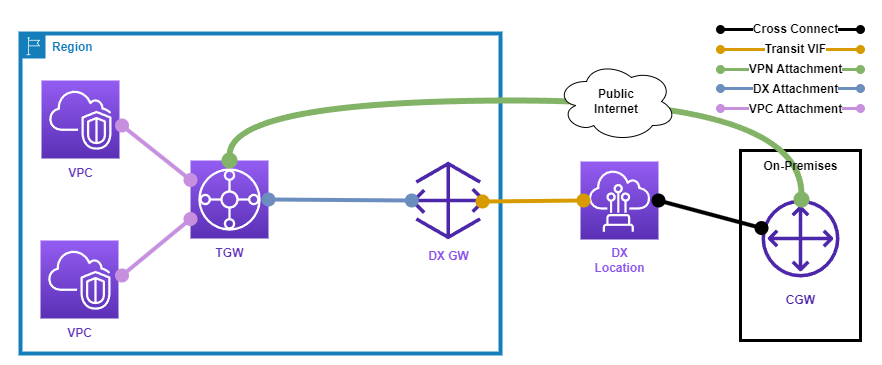
My notes on AWS Transit Gateway can be found here.
Virtual Private Gateway
AWS Virtual Private Gateway is a managed service that allows you to connect a VPC to an on-premises network via a VPN or Direct Connect connection.
The following diagram shows an example AWS Virtual Private Gateway topology.
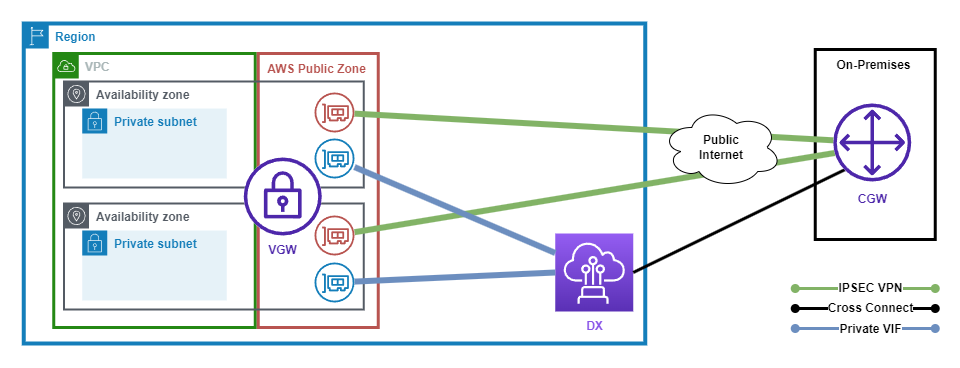
My notes on AWS Virtual Private Gateway can be found here.
Direct Connect
AWS Direct Connect is a managed service that allows you to connect a VPC to an on-premises network via a dedicated or partner managed, private connection.
The following diagram shows an example AWS Direct Connect topology.
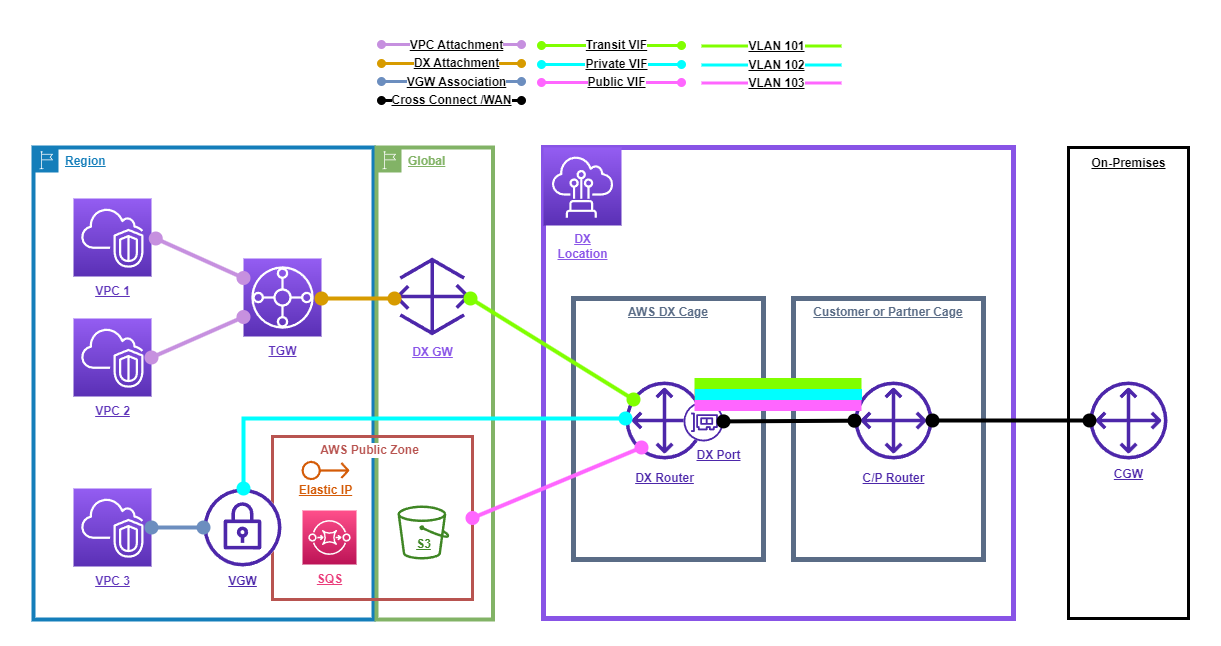
My notes on AWS Direct Connect can be found here.
Route 53
AWS Route 53 is a managed DNS service that allows you to manage domain names as well as act as DNS resolver for your VPCs and on-premises networks.
My notes on AWS Route 53 can be found here.
CloudFront
AWS CloudFront is a managed CDN service that allows you to cache content close to the users via a CloudFront distribution.
My notes on AWS CloudFront can be found here.
Links
https://learn.cantrill.io/courses/1231680/lectures/31757251
https://aws.amazon.com/about-aws/global-infrastructure/?p=ngi&loc=0
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/local-zones/latest/ug/what-is-aws-local-zones.html
https://aws.amazon.com/outposts/
https://docs.aws.amazon.com/global-accelerator/latest/dg/what-is-global-accelerator.html